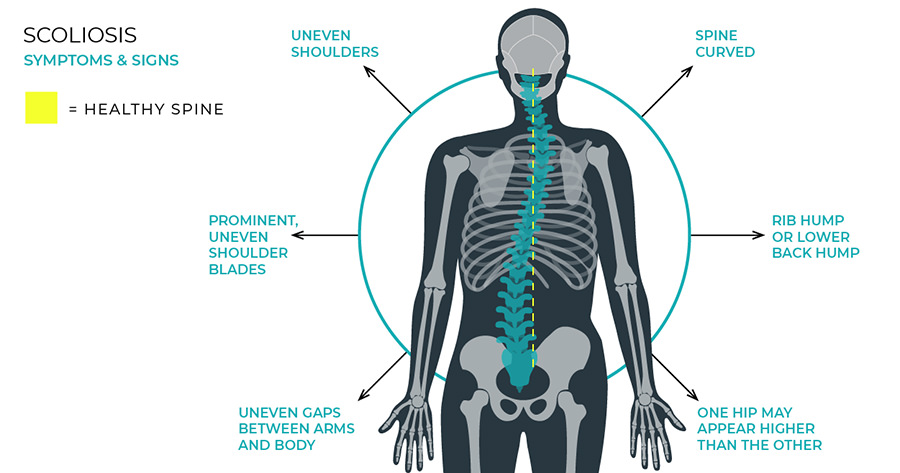
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. It can affect people of all ages, but it typically develops during adolescence. The condition can have a significant impact on daily life, causing pain, discomfort, and limitations in mobility. Scoliosis can also affect a person’s self-esteem and body image, leading to emotional and psychological challenges.
Understanding the role of physical therapy in scoliosis treatment
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of scoliosis. While it cannot cure the condition, targeted physical therapy can help alleviate symptoms, improve spinal alignment, and enhance overall quality of life for scoliosis patients. Physical therapists are trained to assess and address the specific needs of individuals with scoliosis, tailoring treatment plans to their unique circumstances.
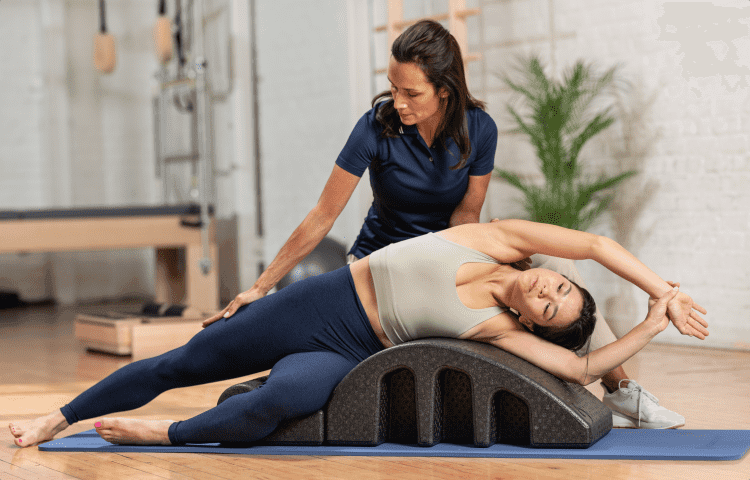

The benefits of targeted physical therapy for scoliosis patients
Targeted physical therapy offers numerous benefits for scoliosis patients. One of the primary advantages is pain relief. Scoliosis can cause muscle imbalances, joint dysfunction, and nerve compression, leading to chronic pain and discomfort. Physical therapy techniques such as manual therapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises can help alleviate these symptoms, improving the patient’s overall comfort and well-being.
In addition to pain relief, physical therapy can also improve posture and spinal alignment. Scoliosis often results in a forward or sideways curvature of the spine, leading to an asymmetrical posture. Physical therapists can design exercises and stretches that target specific muscle groups to correct imbalances and promote better alignment. This can help reduce the progression of the curvature and improve the patient’s overall posture.
How physical therapy can alleviate pain and discomfort associated with scoliosis
Physical therapy offers various techniques to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with scoliosis. Manual therapy, which includes hands-on techniques such as massage and joint mobilization, can help relieve muscle tension, reduce inflammation, and improve joint mobility. These techniques can provide immediate pain relief and improve the patient’s overall range of motion.
Strengthening exercises are another essential component of physical therapy for scoliosis. By targeting specific muscle groups, such as the core, back, and hips, these exercises can help improve stability, support the spine, and reduce strain on the affected areas. Strengthening exercises can also help correct muscle imbalances, which are common in scoliosis patients, and improve overall body mechanics.
Stretching techniques to increase flexibility and reduce muscle imbalances
Stretching is a vital component of physical therapy for scoliosis. It helps increase flexibility, reduce muscle imbalances, and improve overall range of motion. By stretching tight muscles and strengthening weak ones, physical therapists can help restore balance and symmetry to the body. This can alleviate pain, improve posture, and enhance the patient’s ability to perform daily activities.
Manual therapy techniques for pain relief and improved mobility
Manual therapy techniques, such as massage, joint mobilization, and myofascial release, can provide significant pain relief and improve mobility for scoliosis patients. These hands-on techniques help release muscle tension, reduce inflammation, and improve joint mobility. By targeting specific areas of the body, physical therapists can address the underlying causes of pain and discomfort, promoting better overall function and mobility.
The importance of core stabilization exercises in scoliosis management
Core stabilization exercises are crucial for scoliosis management. The core muscles, including the abdominals, back muscles, and pelvic floor, provide stability and support to the spine. Strengthening these muscles can help improve posture, reduce strain on the spine, and enhance overall body mechanics. Core stabilization exercises can also help prevent further progression of the curvature and improve the patient’s ability to perform daily activities.
Postural education and body mechanics training for scoliosis patients
Postural education and body mechanics training are essential components of physical therapy for scoliosis. Physical therapists can educate patients on proper posture and body mechanics to minimize strain on the spine and reduce the risk of injury. They can also provide guidance on ergonomic modifications and assistive devices that can support the patient’s daily activities and promote optimal spinal alignment.
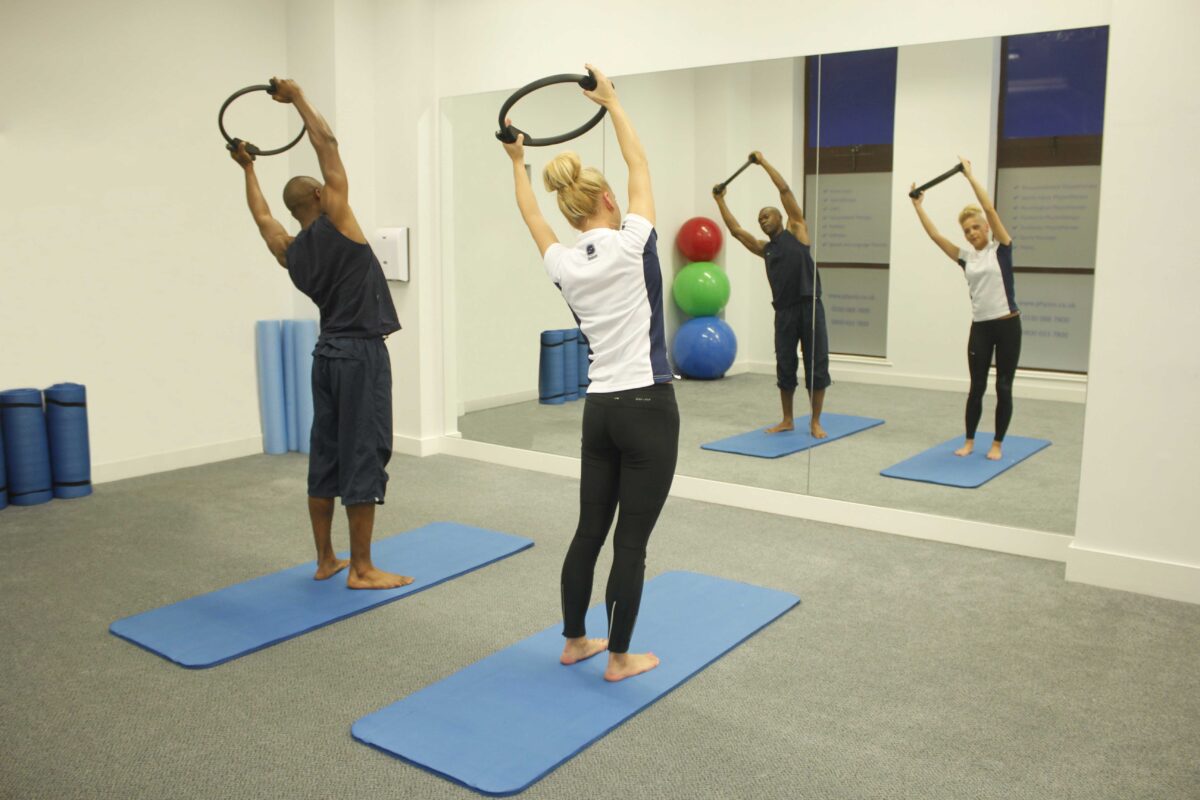

Incorporating scoliosis-specific exercises into a comprehensive treatment plan
Physical therapists can design scoliosis-specific exercises to address the unique needs of each patient. These exercises may include specific stretches, strengthening exercises, and postural correction techniques tailored to the individual’s curvature and symptoms. By incorporating these exercises into a comprehensive treatment plan, physical therapists can help scoliosis patients manage their condition effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
The role of physical therapy in pre and post-surgical scoliosis care
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in both pre and post-surgical scoliosis care. Before surgery, physical therapists can help prepare the patient’s body for the procedure by improving strength, flexibility, and overall physical condition. This can enhance the surgical outcome and facilitate the recovery process.
After surgery, physical therapy is essential for rehabilitation and recovery. Physical therapists can help manage pain, restore mobility, and gradually reintroduce physical activity. They can also provide guidance on proper body mechanics and postural correction to prevent complications and promote optimal healing.
Conclusion: The potential of targeted physical therapy in supporting scoliosis treatment
Targeted physical therapy offers significant potential in supporting scoliosis treatment. By addressing pain, improving posture, and enhancing overall function, physical therapy can alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for scoliosis patients. With a comprehensive treatment plan that includes stretching, strengthening exercises, manual therapy techniques, and postural education, physical therapists can help individuals with scoliosis manage their condition effectively and achieve better long-term outcomes.
References
- Weiss HR, Goodall D. “Current options for the conservative management of scoliosis (3–16 years).” Scoliosis. 2008;3:6. doi: 10.1186/1748-7161-3-6.
- Negrini S, Aulisa AG, Rossi S, et al. “Bracing in idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review.” European Spine Journal. 2015;24(1):34-40. doi: 10.1007/s00586-014-3406-8.
- Kuru T, Yeldan İ, Kaya A, et al. “The effects of physiotherapy on idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review.” Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders. 2018;13:13. doi: 10.1186/s13013-018-0145-2.
- Monticone M, Ambrosini A, Cazzaniga D, Rocca B, Ferrante S. “A comprehensive rehabilitation program vs. a home-based exercise program for patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled trial.” Scoliosis. 2016;11:20. doi: 10.1186/s13013-016-0075-4.
- Mazières B, Hachem R, Gosselin S, et al. “Efficacy of a scoliosis-specific exercise program on curve progression and back pain in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled trial.” Spine. 2017;42(7):504-511. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001843.
- Bezer M, Apaydın Z, Cömert S, et al. “The impact of scoliosis-specific exercises on scoliosis and quality of life: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.” European Spine Journal. 2020;29(4):760-770. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-06014-5.
- Dobbs MB, Rairigh J, N. P, et al. “Surgical and non-surgical treatment of scoliosis: A review of evidence-based outcomes.” Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2014;34(5):519-525. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000227.

