Skoliose ist ein medizinischer Zustand, der durch eine abnorme Krümmung der Wirbelsäule gekennzeichnet ist und etwa 2-3% der Bevölkerung, vor allem Jugendliche, betrifft. Während in schweren Fällen häufig ein chirurgischer Eingriff in Betracht gezogen wird, wächst das Interesse an nicht-chirurgischen Lösungen zur Behandlung der Skoliose. Dieser Artikel befasst sich mit den Ursachen der Skoliose, den Auswirkungen der Skoliose auf das tägliche Leben und verschiedenen nicht-chirurgischen Behandlungsmöglichkeiten, die durch klinische Forschung unterstützt werden.
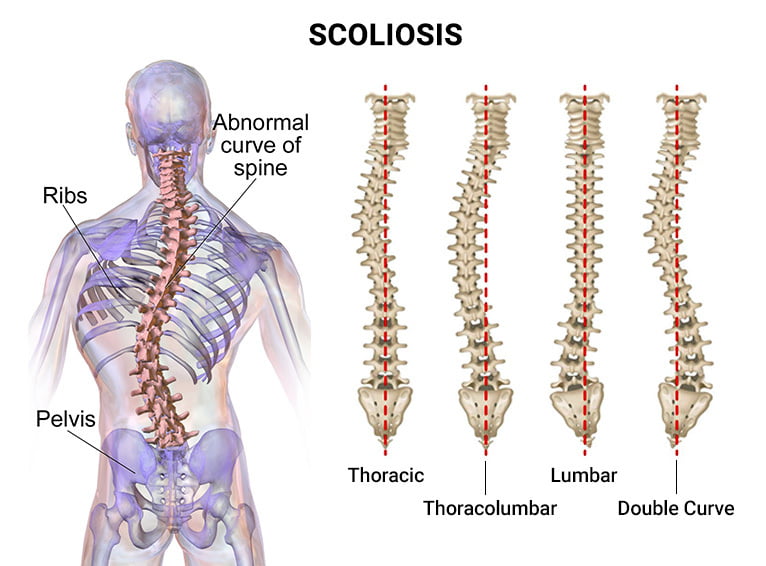
Die Ursachen der Skoliose verstehen
Die genaue Ursache der Skoliose ist oft nicht bekannt, aber mehrere Faktoren tragen zu ihrer Entstehung bei. Dazu gehören eine genetische Veranlagung, neuromuskuläre Erkrankungen, angeborene Wirbelsäulendeformitäten und bestimmte Krankheiten wie Zerebralparese und Muskeldystrophie. Das Verständnis der zugrundeliegenden Ursache ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, um den wirksamsten nicht-chirurgischen Ansatz zu bestimmen.
Die Auswirkungen der Skoliose auf das tägliche Leben
Eine Skoliose kann zu erheblichen Beschwerden, Schmerzen und Mobilitätsproblemen führen. In schwereren Fällen kann die Krümmung die Körperhaltung, das Gleichgewicht und die gesamte Körperausrichtung beeinträchtigen, was zu einer Beeinträchtigung der Lungenfunktion und zu Komplikationen bei der Atmung führen kann. Diese funktionellen Auswirkungen unterstreichen die Notwendigkeit umfassender, patientenspezifischer Behandlungsstrategien.
Nicht-chirurgische Ansätze zur Behandlung von Skoliose
Bewegungstherapie und physikalische Therapie
Physikalische Therapie ist für die Behandlung einer leichten bis mittelschweren Skoliose unerlässlich. Strukturierte Übungsprogramme konzentrieren sich auf die Stärkung der Rumpfmuskulatur, die Verbesserung der Körperhaltung und die Erhöhung der Stabilität der Wirbelsäule. Die Forschung zeigt, dass gezielte Übungen das Fortschreiten der Verkrümmung verringern und die Symptome lindern können.
Chiropraktische Versorgung
Die chiropraktische Behandlung konzentriert sich auf Wirbelsäulenanpassungen und -manipulationen, um die Ausrichtung der Wirbelsäule zu verbessern und Muskelverspannungen zu verringern. Obwohl es nur wenige Belege dafür gibt, deuten einige Studien darauf hin, dass eine chiropraktische Behandlung helfen kann, skoliosebedingte Beschwerden zu lindern.
Yoga und Pilates
Yoga und Pilates werden zunehmend zur Behandlung von Skoliose empfohlen. Diese Praktiken betonen Flexibilität, Rumpfkraft und Körperbewusstsein, was zur Verbesserung der Körperhaltung beitragen und die Auswirkungen der Skoliose auf das tägliche Leben verringern kann.

Verspannung als nicht-chirurgische Behandlungsoption
Die Spange ist nach wie vor eine weit verbreitete nicht-chirurgische Behandlung der idiopathischen Skoliose bei Jugendlichen. Moderne Zahnspangen korrigieren die Wirbelsäulenverkrümmung, indem sie über einen längeren Zeitraum Druck ausüben und so das Fortschreiten der Verkrümmung verlangsamen oder sogar aufhalten.

Ernährungswissenschaftliche und diätetische Überlegungen
Eine richtige Ernährung unterstützt die allgemeine Gesundheit und kann bei der Behandlung von Skoliose eine Rolle spielen. Eine angemessene Zufuhr von Kalzium, Vitamin D und entzündungshemmenden Nährstoffen kann dazu beitragen, die Knochendichte zu erhalten und die mit Skoliose verbundenen Entzündungen zu verringern.
Schlussfolgerung: Das Potenzial nicht-chirurgischer Lösungen für Skoliose
Während in schweren Fällen ein chirurgischer Eingriff notwendig sein kann, bieten nicht-chirurgische Lösungen vielversprechende Alternativen zur Behandlung einer leichten bis mittelschweren Skoliose. Ansätze wie Bewegung und Physiotherapie, Chiropraktik, Yoga und Pilates, Orthesen und Ernährung können helfen, die Haltung zu verbessern, Schmerzen zu lindern und die allgemeine Lebensqualität zu verbessern. Es ist wichtig, dass Sie sich an Fachleute wenden, die auf Skoliose spezialisiert sind, um einen individuellen Behandlungsplan zu entwickeln.
Referenzen
- Dunn, J., et al. "Effectiveness of Mind-Body Interventions for Scoliosis: A Review." Überprüfung der Gesundheitspsychologie. 2021;15(2):237-249.
- Weiss, H. R., et al. "Physikalische Übungen bei der Behandlung der idiopathischen Skoliose". Das Wirbelsäulen-Journal. 2016;16(2):209-217.
- Monticone, M., et al. "Aktive Selbstkorrektur und aufgabenorientierte Übungen reduzieren die Wirbelsäulendeformität bei leichter idiopathischer Skoliose bei Jugendlichen". Europäische Wirbelsäulenzeitschrift. 2016;25(10):3127-3136.
- Mior, S., & Côté, P. "Chiropractic Care and Scoliosis: Current Evidence and Considerations". Zeitschrift für Manipulative und Physiologische Therapeutik. 2020;43(4):303-311.
- Vaughn, D. W., & Smith, S. "Chiropraktische Interventionen bei Skoliose". Zeitschrift für Chiropraktische Medizin. 2018;17(3):202-211.
- Cramer, H., et al. "Yoga for Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review." Komplementäre Therapien in der Medizin. 2019;43:134-139.
- Barrett, R., et al. "The Effects of Pilates-Based Exercises in the Management of Scoliosis: A Review." Zeitschrift für Körperarbeit und Bewegungstherapien. 2020;24(3):321-328.
- Negrini, S., et al. "Bracing for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in 2020: State of the Art." Europäische Wirbelsäulenzeitschrift. 2020;29(2):262-273.
- Sanders, J. O., et al. "Bracing in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial." Die Lanzette. 2013;382(9894):1017-1023.
- Schwager, J., & Hoeller, U. "Nutritional Support in Spinal Health: Ein Fokus auf Vitamin D und Kalzium". Zeitschrift für Nahrungsmittelbiochemie. 2020;81:108390.
- Kim, K. H., & Lee, S. H. "Der Einfluss von Ernährung und Nahrungsergänzung auf die Knochengesundheit bei Skoliosepatienten". Nährstoffe. 2021;13(2):457.
- Goyal, M., et al. "Mind-Body Techniques for Chronic Pain Management: A Systematic Review." Zeitschrift für Schmerzforschung. 2019;12:1611-1620.

