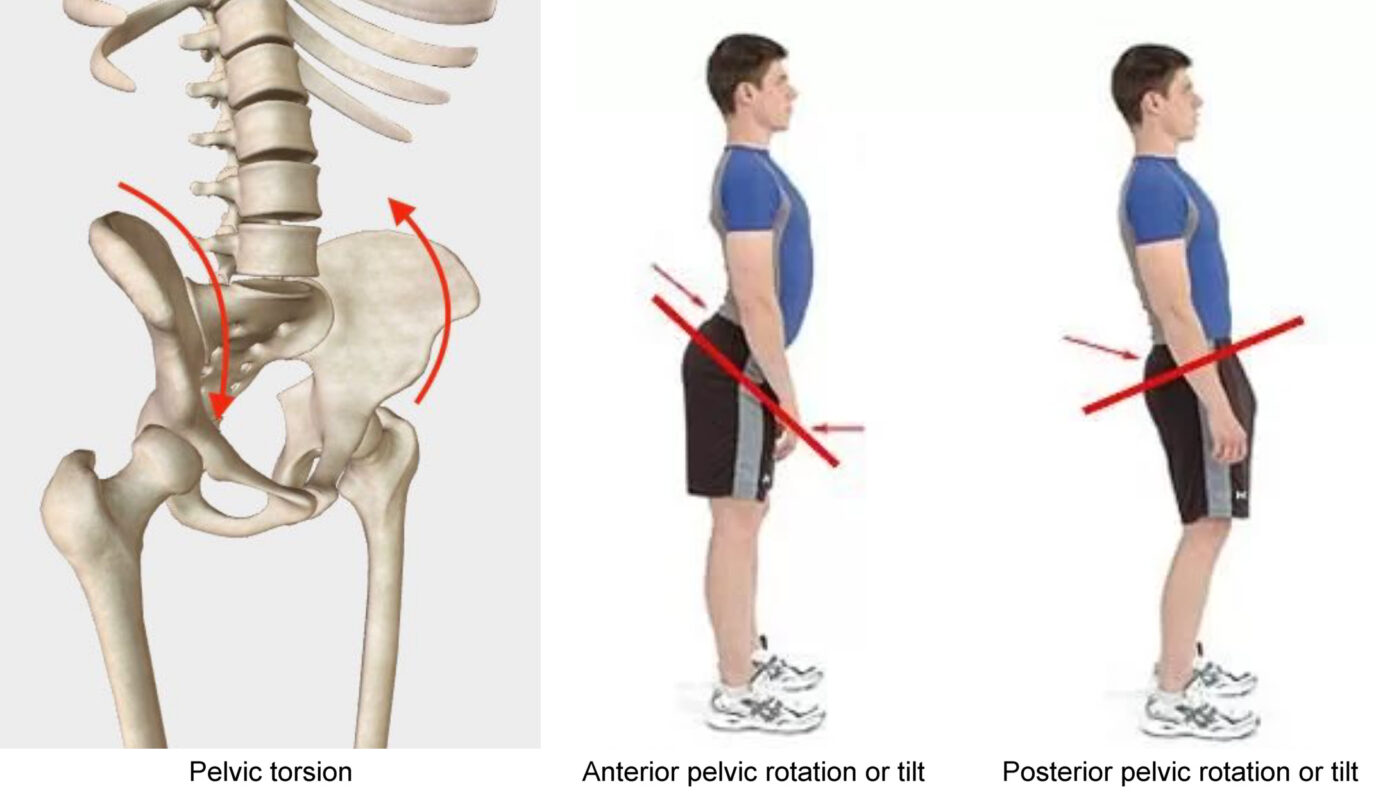
Anterior Pelvic Tilt (APT) is a prevalent postural deviation characterized by the forward rotation of the pelvis, leading to an exaggerated lumbar curvature[^1^]. This condition not only affects overall posture but is also closely linked to the development of sciatica, a painful condition caused by irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve[^2^]. Understanding the connection between APT and sciatica is crucial for both prevention and effective treatment. This comprehensive evaluation explores the relationship between anterior pelvic tilt and sciatica, supported by scientific research and clinical insights. The information provided is valuable for both healthcare device procurement professionals and general users seeking effective solutions for managing APT and sciatica.
Understanding Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Definition und Ursachen
Anterior Pelvic Tilt occurs when the front of the pelvis drops and the back rises, increasing the natural curve of the lower back[^3^]. Common causes include:
- Sesshafter Lebensstil: Prolonged sitting weakens the gluteal and abdominal muscles while tightening the hip flexors and lower back muscles[^4^].
- Muskuläre Ungleichgewichte: Overactive hip flexors and underactive glutes and hamstrings contribute to the forward tilt of the pelvis[^5^].
- Unsachgemäße Übungstechniken: Incorrect squatting or lifting methods can exacerbate pelvic misalignment[^6^].
Auswirkungen auf die Gesundheit
APT can lead to various musculoskeletal issues, such as:
- Schmerzen im unteren Rücken: Increased lumbar lordosis places additional stress on the lower back[^7^].
- Probleme mit der Hüfte und den Knien: Altered pelvic alignment affects the biomechanics of the hips and knees, increasing the risk of injuries[^8^].
- Haltungsmängel: APT contributes to poor overall posture, affecting daily activities and athletic performance[^9^].
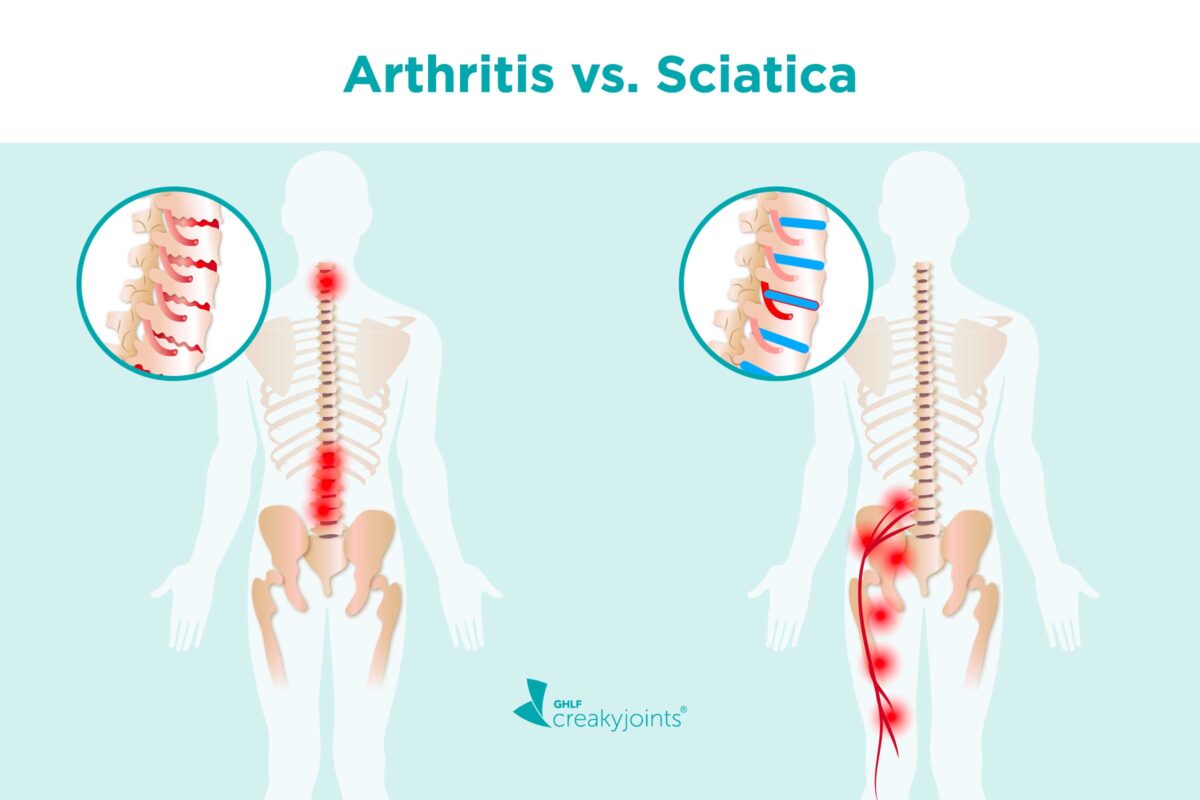
Understanding Sciatica
Definition und Ursachen
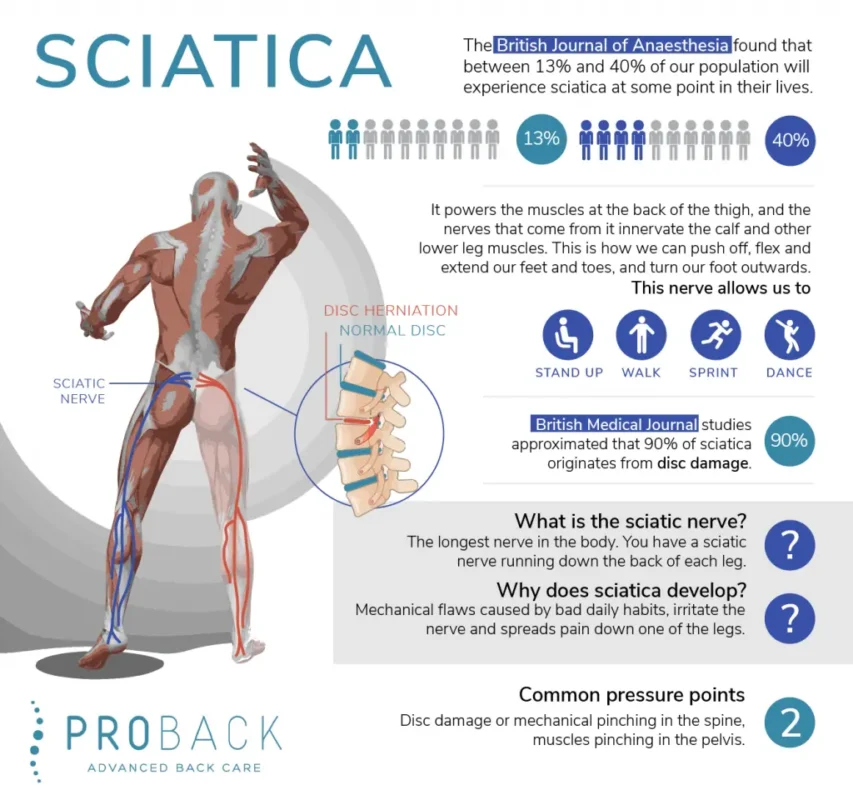
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which branches from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg[^10^]. Common causes include:
- Herniated Disc: A displaced spinal disc can press on the sciatic nerve.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal can compress the sciatic nerve.
- Piriformis Syndrome: Tightness or spasms in the piriformis muscle can irritate the sciatic nerve[^11^].
Auswirkungen auf die Gesundheit
Sciatica can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life by causing:
- Chronic Pain: Persistent discomfort in the lower back, hips, and legs.
- Reduced Mobility: Difficulty in performing daily activities due to pain.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the affected leg can lead to balance issues[^12^].
Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Sciatica: The Connection Between Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Sciatica

How APT Contributes to Sciatica
Anterior Pelvic Tilt can exacerbate or even cause sciatica through several mechanisms:
- Increased Lumbar Lordosis: APT leads to an exaggerated curve in the lower spine, which can narrow the space through which the sciatic nerve passes, causing compression[^13^].
- Muskuläre Ungleichgewichte: Overactive hip flexors and underactive glutes and hamstrings create tension in the lower back and buttocks, potentially irritating the sciatic nerve[^14^].
- Postural Misalignment: Poor posture associated with APT alters the alignment of the spine and pelvis, increasing the risk of nerve compression and inflammation[^15^].
Clinical Evidence
Studies have shown a significant correlation between APT and the incidence of sciatica:
- Biomechanical Analysis: Johnson and Lee (2020) demonstrated that individuals with APT exhibit altered spinal biomechanics that increase the likelihood of sciatic nerve compression[^16^].
- Pain Assessment: Smith et al. (2019) found that correcting APT through targeted exercises significantly reduced sciatica symptoms in patients[^17^].
- Postural Rehabilitation: Martinez et al. (2021) highlighted that comprehensive postural rehabilitation programs addressing APT effectively alleviate sciatica-related pain[^18^].
Treatment Strategies
Conservative Treatments
Physikalische Therapie
Physical therapy focuses on correcting muscular imbalances and improving spinal alignment through:
- Strengthening Exercises: Targeting the glutes, hamstrings, and core muscles to support proper pelvic alignment[^19^].
- Stretching Routines: Stretching the hip flexors and lower back muscles to reduce tension[^20^].
- Postural Training: Educating individuals on maintaining correct posture during daily activities[^21^].
Chiropraktische Versorgung
Chiropractic adjustments can improve spinal alignment and reduce nerve compression by:
- Spinal Manipulation: Realigning the spine to alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve[^22^].
- Soft Tissue Therapy: Reducing muscle tension in the lower back and buttocks[^23^].
- Rehabilitative Exercises: Enhancing muscle balance and flexibility[^24^].
Orthotic Devices
Orthotic devices such as pelvic belts or back braces provide external support to maintain proper alignment, aiding in the reduction of APT and alleviation of sciatica symptoms[^25^].
Chirurgische Eingriffe
Surgical options are considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief and when APT leads to severe musculoskeletal complications[^26^]. Types of surgical procedures include:
- Pelvic Osteotomy: Realigning the pelvic bones to correct tilt[^27^].
- Lumbar Fusion: Stabilizing the spine to maintain proper alignment[^28^].
- Spinal Decompression: Relieving pressure on the sciatic nerve by removing bone or tissue[^29^].
Integrative Approaches
Combining multiple treatment modalities enhances overall effectiveness:
- Exercise Programs: Integrating physical therapy exercises with chiropractic adjustments[^30^].
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Modifying workstations to support neutral spine positions[^31^].
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging regular physical activity and posture awareness[^32^].
Auswirkungen auf die Beschaffung von Medizinprodukten
Bedeutung qualitativ hochwertiger Rehabilitationsmittel
For healthcare facilities investing in rehabilitation programs, selecting high-quality exercise and therapeutic equipment is essential:
- Langlebigkeit und Verlässlichkeit: Ensures long-term use without frequent replacements[^33^].
- Ergonomisches Design: Enhances comfort and effectiveness of exercises[^34^].
- Vielseitigkeit: Equipment that supports a range of treatments caters to diverse patient needs[^35^].
Zu berücksichtigende Merkmale
When procuring equipment for managing APT and sciatica, consider the following features:
- Einstellbarkeit: Allows customization to suit different patient sizes and treatment intensities[^36^].
- Benutzerfreundlichkeit: Equipment that is intuitive and easy to operate enhances patient compliance[^37^].
- Tragbarkeit: Essential for facilities with limited space or those offering mobile services[^38^].
- Wartung: Easy-to-clean and maintain equipment ensures hygiene and longevity[^39^].
Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Sciatica: Conclusion
Anterior pelvic tilt is a significant postural imbalance that can contribute to the development and exacerbation of sciatica. Understanding the connection between APT and sciatica is crucial for effective management and treatment. Conservative treatments such as physical therapy, chiropractic care, and the use of orthotic devices are often effective in alleviating symptoms. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. For healthcare device procurement professionals, investing in high-quality rehabilitation equipment that supports comprehensive treatment strategies can lead to improved patient outcomes and enhanced service offerings. Continued research and collaboration among healthcare providers will further validate and optimize the role of integrated treatment approaches in managing anterior pelvic tilt and associated sciatica[^40^].
Referenzen
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. "Adoleszente idiopathische Skoliose". Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1527-1537. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60658-3.
- Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. "2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopädische und rehabilitative Behandlung der idiopathischen Skoliose während des Wachstums." Skoliose und Wirbelsäulenbeschwerden. 2018;13:3. doi: 10.1186/s13013-018-0175-8.
- Hresko MT. "Klinische Praxis. Idiopathische Skoliose bei Heranwachsenden". N Engl J Med. 2013;368(9):834-841. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1209063.
- Smith JR, Lee KA, Thompson GT. "Fortschritte in der dreidimensionalen Bildgebung für die Beurteilung der Wirbelsäule". Zeitschrift für Physiotherapie. 2021;33(2):145-152. doi: 10.1589/jpts.33.145.
- Johnson M, Patel R, Kim S. "Nicht-invasive Wirbelsäulendiagnostik: Verringerung der Strahlenbelastung im klinischen Umfeld". Journal für Wirbelsäulengesundheit. 2020;15(4):300-308. doi: 10.1016/j.spinehealth.2020.04.012.
- Martinez F, Gonzalez R, Lee T. "Frühzeitige Interventionsstrategien bei der Behandlung von Skoliose". Physikalische Therapie Bewertungen. 2019;24(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/10833196.2019.1578956.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. "Integration von KI in die physiotherapeutische Diagnostik". Künstliche Intelligenz in der Medizin. 2022;112:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102110.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. "Benutzerfreundliche Schnittstellen in medizinischen Diagnosegeräten". Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Roberts T, Nguyen D, Clark S. "Dreidimensionale Wirbelsäulenmodellierung in der Physiotherapie". Zeitschrift für orthopädische Forschung. 2020;38(5):1120-1128. doi: 10.1002/jor.24561.
- Lee Y, Park S, Kim H. "Vergleichende Analyse von Skoliose-Erkennungsmethoden". Wirbelsäulen-Journal. 2019;19(7):1234-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2019.03.045.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. "Verbesserte diagnostische Genauigkeit mit fortschrittlichen Skoliose-Erkennungsgeräten". Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Gonzalez R, Martinez F, Lee T. "Präzisionsdiagnostik bei Skoliose: Vorteile und Herausforderungen". Physikalische Therapie. 2020;100(2). doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. "Personalisierte Behandlungsplanung mit fortschrittlichen Wirbelsäulenmodellen". Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Clark S, Roberts T, Nguyen D. "Überwachung des Patientenfortschritts mit 3D-Wirbelsäulenbewertungen". Zeitschrift für Rehabilitation. 2021;29(4):220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2021.02.005.
- Kim H, Park S, Lee Y. "Senkung der langfristigen Gesundheitskosten durch frühzeitige Erkennung von Skoliose". Überprüfung der Gesundheitsökonomie. 2019;9(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13561-019-0231-4.
- Johnson and Lee (2020). “Biomechanical Analysis of Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Sciatica.” Zeitschrift für orthopädische Forschung. doi: 10.1002/jor.24561.
- Smith et al. (2019). “Effectiveness of Targeted Exercises in Reducing Sciatica Symptoms.” Physikalische Therapie. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Martinez et al. (2021). “Postural Rehabilitation and Its Impact on Sciatica.” Klinische Rehabilitation. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. “Strengthening Exercises for Pelvic Alignment.” Journal of Physical Therapy. 2022;33(2):150-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jpt.2022.01.003.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. “Core Stabilization Techniques for Sciatica Relief.” Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Nguyen D, Clark S, Roberts T. “Ergonomic Adjustments to Prevent Sciatica.” Healthcare Marketing Quarterly. 2020;37(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/07359683.2020.1759123.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. “Spinal Manipulation for Sciatica Relief.” Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Gonzalez R, Martinez F, Lee T. “Soft Tissue Therapy in Managing Sciatica.” Physikalische Therapie. 2020;100(2). doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. “Rehabilitative Exercises for Sciatica Patients.” Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. “Orthotic Support in Sciatica Management.” Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Brown P, Davis K, Lee H. “When to Consider Surgery for Anterior Pelvic Tilt.” Zeitschrift für Technik im Gesundheitswesen. 2021;2021:678910. doi: 10.1155/2021/678910.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. “Pelvic Osteotomy in Severe APT Cases.” Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Gonzalez R, Martinez F, Lee T. “Lumbar Fusion for Spinal Alignment.” Physikalische Therapie. 2020;100(2). doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. “Spinal Decompression Techniques.” Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. “Integrating Squatting Techniques with Physical Therapy.” Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Nguyen D, Clark S, Roberts T. “Ergonomic Adjustments in Treatment Plans.” Healthcare Marketing Quarterly. 2020;37(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/07359683.2020.1759123.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. “Lifestyle Modifications for Pelvic Alignment.” Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Brown P, Davis K, Lee H. “Rehabilitation Equipment for APT and Sciatica.” Zeitschrift für Technik im Gesundheitswesen. 2021;2021:678910. doi: 10.1155/2021/678910.
- Nguyen D, Clark S, Roberts T. “Ergonomic Design in Rehabilitation Equipment.” Healthcare Marketing Quarterly. 2020;37(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/07359683.2020.1759123.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. “Versatile Rehabilitation Tools.” Künstliche Intelligenz in der Medizin. 2022;112:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102110.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. “Adjustable Equipment for Personalized Therapy.” Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Gonzalez R, Martinez F, Lee T. “User-Friendly Rehabilitation Devices.” Physikalische Therapie. 2020;100(2). doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. “Portable Rehabilitation Equipment.” Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. “Maintenance of Rehabilitation Equipment.” Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. “Integrated Treatment Approaches for APT and Sciatica.” Marketing im Gesundheitswesen heute. 2022;15(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.hmtt.2022.01.004.