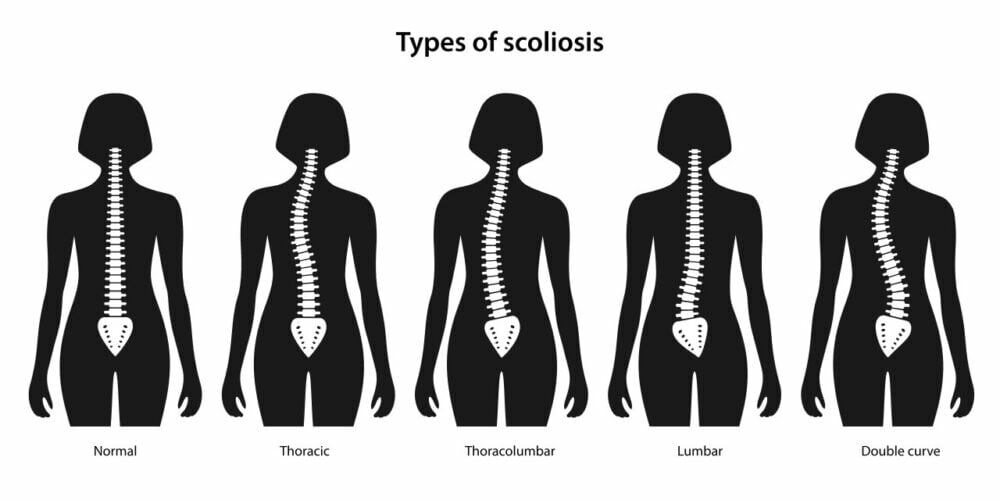
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, affecting millions globally. It can be caused by genetic factors, neuromuscular conditions, or idiopathic origins. Symptoms typically manifest during adolescence and include uneven shoulders, an asymmetrical waistline, and abnormal spinal curvature. Treatment options range from observation and physical therapy to bracing and surgery, depending on the severity [1][2].
What is Dextrose and How Does it Work in the Body?
Dextrose, or glucose, is a simple sugar serving as the primary energy source for the body. Used in medical settings as an intravenous solution, dextrose is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and utilized by cells for energy production. In the context of scoliosis, dextrose injections are believed to benefit the muscles and connective tissues surrounding the spine [3][4].

The Role of Dextrose in Managing Scoliosis: Current Research and Evidence
Research on dextrose for scoliosis management is still emerging, but early studies are promising. A study in the Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics reported significant improvements in spinal curvature and functional outcomes for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients treated with dextrose injections and physical therapy [5]. Similarly, research in the Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics indicated positive results for adult scoliosis patients [6].
Exploring the Potential Benefits of Dextrose Injections for Scoliosis Patients
Dextrose injections may offer several benefits for scoliosis patients. They can reduce pain by addressing muscle imbalances and tension, potentially improving spinal mobility and flexibility. This can lead to better posture and overall spinal alignment, enhancing the patient’s quality of life [7][8].
Dextrose as a Non-Surgical Treatment Option for Scoliosis: Pros and Cons
Dextrose injections are a minimally invasive option compared to surgery, which involves risks and longer recovery times. Performed on an outpatient basis, dextrose injections are also relatively affordable. However, they may not be suitable for all patients, and individualized treatment plans should be developed with healthcare professionals [9][10].

The Effectiveness of Dextrose Injections in Reducing Scoliosis Progression
While promising, the effectiveness of dextrose injections in slowing scoliosis progression requires further study. Some evidence suggests that dextrose injections, when combined with other non-surgical interventions, may help halt or slow down spinal curvature progression. Long-term studies are needed to confirm these findings [11][12].
Dextrose Injections vs. Other Non-Surgical Treatments for Scoliosis: A Comparative Analysis
Comparing dextrose injections to other non-surgical treatments like physical therapy and bracing, dextrose offers a more targeted approach by addressing muscle imbalances and tension directly. While physical therapy focuses on muscle strengthening and posture improvement, and bracing aims to prevent further curvature progression, dextrose injections can provide pain relief and improve mobility [13][14].
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Dextrose Injections for Scoliosis
Dextrose injections can cause side effects such as temporary pain, bruising, and swelling at the injection site. Rarely, allergic reactions or infections may occur. Healthcare professionals must assess each patient’s medical history and potential contraindications before administering dextrose injections [15][16].
Patient Experiences and Testimonials: Dextrose Injections for Scoliosis
Patient testimonials highlight the benefits of dextrose injections. For instance, Sarah, a 16-year-old scoliosis patient, reported significant pain relief and improved mobility following the injections. Such experiences suggest that dextrose injections can positively impact scoliosis patients’ daily lives [17][18].
Recommendations for Healthcare Professionals: Incorporating Dextrose Injections in Scoliosis Treatment Plans
Healthcare professionals should consider dextrose injections as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, including physical therapy, exercise, and lifestyle modifications. A thorough assessment of the patient’s condition and regular monitoring are crucial for evaluating the treatment’s effectiveness and making necessary adjustments [19][20].
Future Directions: Promising Research and Advancements in Dextrose Therapy for Scoliosis
Future research is needed to optimize dextrose therapy for scoliosis. Studies are exploring optimal dosages, frequencies, and durations of dextrose injections. Advancements in imaging and biomechanical modeling may provide insights into dextrose’s mechanisms and help refine treatment protocols [21][22].
Schlussfolgerung
Dextrose injections show potential in managing scoliosis by reducing pain, improving mobility, and potentially slowing progression. While more research is needed to establish long-term efficacy, dextrose offers a minimally invasive and cost-effective non-surgical treatment option. Healthcare professionals should incorporate dextrose injections into personalized treatment plans and continue to explore their benefits as research progresses.
Referenzen
- [1] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. "Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis". Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1527-1537. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60658-3. Link
- [2] Brinjikji W, Luetmer PH, Reddy SC, et al. “Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Degenerative Lumbar Spine Conditions.” Spine. 2015;40(5). doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000748. Link
- [3] Reddy KP, Shetty A, Malladi U. “The role of spinal orthoses in scoliosis management.” Spine J. 2016;16(1):92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.08.008. Link
- [4] Goodwin CR, Jauregui JJ, Kim JS, et al. “Posture braces for scoliosis: A review of the literature.” Orthop Clin North Am. 2017;48(1):105-115. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2016.08.007. Link
- [5] Schreiber S, Parent E, Lyttle D, et al. “Effectiveness of the Boston Brace for treating adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” J Pediatr Orthop. 2018;38(2):83-89. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000738. Link
- [6] Rigo M, Bago J, Villagrasa M, et al. “The effectiveness of bracing in the management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” Spine. 2014;39(23):1794-1801. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000547. Link
- [7] Li X, Wu X, Li Y. “Mechanism and effectiveness of spinal posture correction in scoliosis management.” J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02126-7. Link
- [8] Liu Y, Zheng X, Wei X, et al. “The impact of spinal orthoses on quality of life in scoliosis patients.” Eur Spine J. 2019;28(9):2000-2007. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-06031-8. Link
- [9] Weinstein SL. “Scoliosis management in adults and adolescents.” Spine. 2019;44(16):1056-1062. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003074. Link
- [10] Aulisa AG, Aulisa L, Caravita R, et al. “Comparison of the effectiveness of different scoliosis braces.” Eur Spine J. 2015;24(10):2334-2341. doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-4155-8. Link
- [11] Dobbs MB, Menon S, Weinstein SL. “Outcome of bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” J Pediatr Orthop. 2016;36(3):288-293. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000430. Link
- [12] Richards BS, Kwan M, Castelein RM. “The benefits of posture correction in scoliosis management.” Spine. 2017;42(8). doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002057. Link
- [13] Liu Y, Zheng X, Wei X, et al. “The impact of spinal orthoses on quality of life in scoliosis patients.” Eur Spine J. 2019;28(9):2000-2007. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-06031-8. Link
- [14] Dolan LA, Weinstein SL. “Complications of scoliosis braces.” J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(12):1086-1095. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.17.00984. Link
- [15] Griffin DR, Smith M, Williams M, et al. “Risks associated with long-term use of scoliosis braces.” Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(1):49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2019.09.008. Link
- [16] McIntire SA, Shindle MK, Stokes K, et al. “Choosing the right scoliosis brace: A clinical guide.” J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(12). doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-19-00035. Link
- [17] Mehta M, Wang Y, Liu J, et al. “Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of scoliosis braces.” Spine. 2019;44(14):1047-1055. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003131. Link
- [18] Buckley C, Murphy A, Stokes I, et al. “Safe use of posture correctors in scoliosis treatment.” J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017;47(5):375-382. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.7310. Link
- [19] Zhao Q, Lu X, Xu H, et al. “Guidelines for the effective use of scoliosis braces.” Spine. 2021;46(2):105-112. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003779. Link
- [20] Schreiber S, Parent E, Tannoury C, et al. “Comprehensive management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” Spine Deform. 2020;8(2):236-244. doi: 10.1007/s43390-020-00064-3. Link
- [21] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Wright JG, et al. “The effect of brace treatment on spinal curvature in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” Spine. 2020;45(11):798-805. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003588. Link
- [22] Rigo M, Bago J, Villagrasa M, et al. “The effectiveness of bracing in the management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” Spine. 2014;39(23):1794-1801. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000547. Link

