Schwere Skoliose Röntgenbild: Severe scoliosis is a complex spinal condition characterized by a significant curvature of the spine. It can have a profound impact on a person’s quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and functional limitations. In order to effectively diagnose and treat severe scoliosis, healthcare professionals rely on various imaging techniques, with X-rays playing a crucial role in the process. X-rays provide valuable information about the degree of curvature, structural abnormalities, and spinal rotation, which are essential for treatment planning. In this article, we will explore what severe scoliosis looks like on X-rays and its impact on treatment planning.
Understanding Severe Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition that causes an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. While mild cases of scoliosis may not cause significant symptoms or require treatment, severe scoliosis can lead to a range of issues, including pain, breathing difficulties, and reduced mobility. Severe scoliosis is typically defined as a curvature of the spine greater than 40 degrees.

Importance of X-Rays in Diagnosis
X-rays are an essential tool in diagnosing severe scoliosis. They provide a detailed image of the spine, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately measure the degree of curvature and identify any structural abnormalities. X-rays also help in assessing spinal rotation and torsion, which can further inform treatment decisions.

X-Ray Imaging Techniques for Severe Scoliosis
When it comes to imaging severe scoliosis, there are several techniques that can be used. The most common technique is the standing posterior-anterior (PA) X-ray, where the patient stands facing the X-ray machine. This technique provides a comprehensive view of the entire spine and allows for accurate measurement of the curvature. Another technique is the lateral X-ray, where the patient stands sideways to the X-ray machine. This technique helps in assessing the sagittal alignment of the spine and identifying any abnormalities in the front-to-back curvature.

Analyzing X-Rays: Key Findings
When analyzing X-rays of severe scoliosis, there are several key findings that healthcare professionals look for. The first is the degree of curvature, which is measured using the Cobb angle. This angle helps determine the severity of the scoliosis and guides treatment decisions. Another important finding is the presence of structural abnormalities, such as wedging of the vertebrae or rotation of the spine. These abnormalities can impact the stability of the spine and may require surgical intervention.
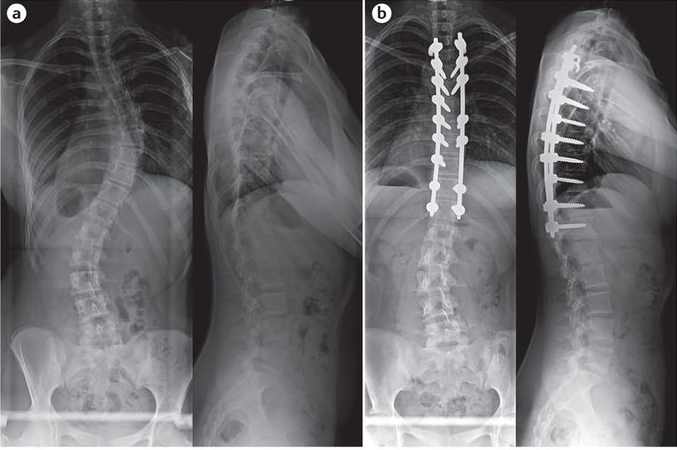
Visualizing Severe Scoliosis on X-Rays
Severe Scoliosis X Ray: Severe scoliosis is visually striking on X-rays. The spine appears curved, with a pronounced sideways deviation. The severity of the curvature can vary, with some cases showing a gentle S-shaped curve, while others exhibit a more pronounced C-shaped curve. The X-rays also reveal the alignment of the vertebrae, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the overall balance of the spine.
Assessing the Degree of Curvature
One of the primary purposes of X-rays in severe scoliosis is to measure the degree of curvature. The Cobb angle, named after the orthopedic surgeon John Cobb, is the most commonly used method for measuring the curvature. It involves drawing lines along the top and bottom of the vertebrae at the apex of the curve and measuring the angle between them. The Cobb angle provides a standardized way to quantify the severity of the scoliosis and helps determine the appropriate treatment approach.
Identifying Structural Abnormalities
X-rays also play a crucial role in identifying structural abnormalities in severe scoliosis. These abnormalities can include wedging of the vertebrae, where the bones become triangular-shaped instead of rectangular, or rotation of the spine, where the vertebrae twist around their axis. These abnormalities can impact the stability of the spine and may require surgical intervention to correct.
Evaluating Spinal Rotation and Torsion
In addition to measuring the degree of curvature and identifying structural abnormalities, X-rays also help in evaluating spinal rotation and torsion. Severe scoliosis often involves a rotational component, where the vertebrae rotate around their axis. This rotation can be visualized on X-rays, providing valuable information about the three-dimensional nature of the deformity. Understanding the degree of rotation is important for treatment planning, as it can influence the surgical approach and the selection of spinal instrumentation.
Implications for Treatment Planning
The information obtained from X-rays of severe scoliosis has significant implications for treatment planning. The degree of curvature, as measured by the Cobb angle, helps determine the appropriate treatment approach. Mild to moderate curves may be managed conservatively with bracing or physical therapy, while severe curves often require surgical intervention. X-rays also help in identifying structural abnormalities that may impact the stability of the spine and guide the selection of surgical techniques and instrumentation.
Surgical Considerations for Severe Scoliosis
In cases where surgical intervention is necessary, X-rays provide crucial information for planning the procedure. The X-rays help in determining the level of the spine where the fusion should start and end. They also aid in selecting the appropriate surgical technique, such as posterior spinal fusion or anterior spinal fusion. X-rays are used during the surgery to guide the placement of screws and other instrumentation, ensuring optimal correction of the curvature.
Schlussfolgerung
Severe scoliosis is a complex spinal condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s life. X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating severe scoliosis by providing valuable information about the degree of curvature, structural abnormalities, and spinal rotation. The information obtained from X-rays guides treatment decisions, including the selection of conservative management or surgical intervention. X-rays also aid in surgical planning, helping determine the appropriate surgical technique and instrumentation. By understanding what severe scoliosis looks like on X-rays and its impact on treatment planning, healthcare professionals can provide the best possible care for individuals with this condition.
Referenzen
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons. “Scoliosis Overview: Diagnosis and Treatment.” AANS. Available at: https://www.aans.org/En/Treatment/Scoliosis
- Mayo Clinic. “Scoliosis: Diagnosis and Treatment.” Mayo Clinic. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/scoliosis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350971
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. “Scoliosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment.” NIH. Available at: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/scoliosis
- Spine-Health. “Understanding Scoliosis: Imaging and Diagnosis.” Spine-Health. Available at: https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/scoliosis/scoliosis-diagnosis
- Cleveland Clinic. “X-Rays for Scoliosis: What to Expect.” Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/13430-x-rays
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. “Scoliosis Imaging Techniques and Analysis.” Johns Hopkins Medicine. Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/scoliosis
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. “Scoliosis: Imaging and Treatment.” AAOS. Available at: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/scoliosis/
- RadiologyInfo.org. “Scoliosis and Spinal Imaging.” RadiologyInfo. Available at: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=scoliosis
- National Scoliosis Foundation. “Imaging for Scoliosis: Techniques and Findings.” NSF. Available at: https://www.scoliosis.org/diagnosis/imaging
- MedlinePlus. “Scoliosis: Diagnostic Imaging.” MedlinePlus. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003238.htm

