Surgery for anterior pelvic tilt: Anterior Pelvic Tilt (APT) is a common postural imbalance characterized by the forward rotation of the pelvis, leading to an exaggerated lumbar curvature[^1^]. Surgery for anterior pelvic tilt: When is Surgical Intervention Necessary. This condition can result in discomfort, reduced mobility, and an increased risk of musculoskeletal injuries[^2^]. While conservative treatments such as physical therapy and chiropractic care are often effective, there are instances where surgical intervention becomes necessary[^3^]. This comprehensive evaluation explores the circumstances under which surgery for APT is warranted, supported by scientific research and clinical insights. The insights provided are valuable for both healthcare device procurement professionals and general users seeking effective solutions for APT.

Understanding surgery for anterior pelvic tilt
Definition und Ursachen
Anterior Pelvic Tilt occurs when the front of the pelvis drops and the back rises, increasing the natural curve of the lower back[^4^]. Common causes include:
- Sesshafter Lebensstil: Prolonged sitting weakens the gluteal and abdominal muscles while tightening the hip flexors and lower back muscles[^5^].
- Muskuläre Ungleichgewichte: Overactive hip flexors and underactive glutes and hamstrings contribute to the forward tilt of the pelvis[^6^].
- Unsachgemäße Übungstechniken: Incorrect squatting or lifting methods can exacerbate pelvic misalignment[^7^].
Auswirkungen auf die Gesundheit
APT can lead to various musculoskeletal issues, such as:
- Schmerzen im unteren Rücken: Increased lumbar lordosis places additional stress on the lower back[^8^].
- Probleme mit der Hüfte und den Knien: Altered pelvic alignment affects the biomechanics of the hips and knees, increasing the risk of injuries[^9^].
- Haltungsmängel: APT contributes to poor overall posture, affecting daily activities and athletic performance[^10^].
Surgical Interventions for Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Indikationen für eine Operation
Surgical intervention for APT is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or when the tilt leads to severe musculoskeletal complications[^11^]. Indications include:
- Severe Pelvic Misalignment: Significant deviation that affects spinal alignment and overall posture[^12^].
- Chronic Pain: Persistent lower back, hip, or knee pain unresponsive to non-surgical therapies[^13^].
- Functional Impairment: Reduced mobility and impaired ability to perform daily activities[^14^].
- Progressive Deformity: Worsening pelvic tilt over time despite conservative management[^15^].
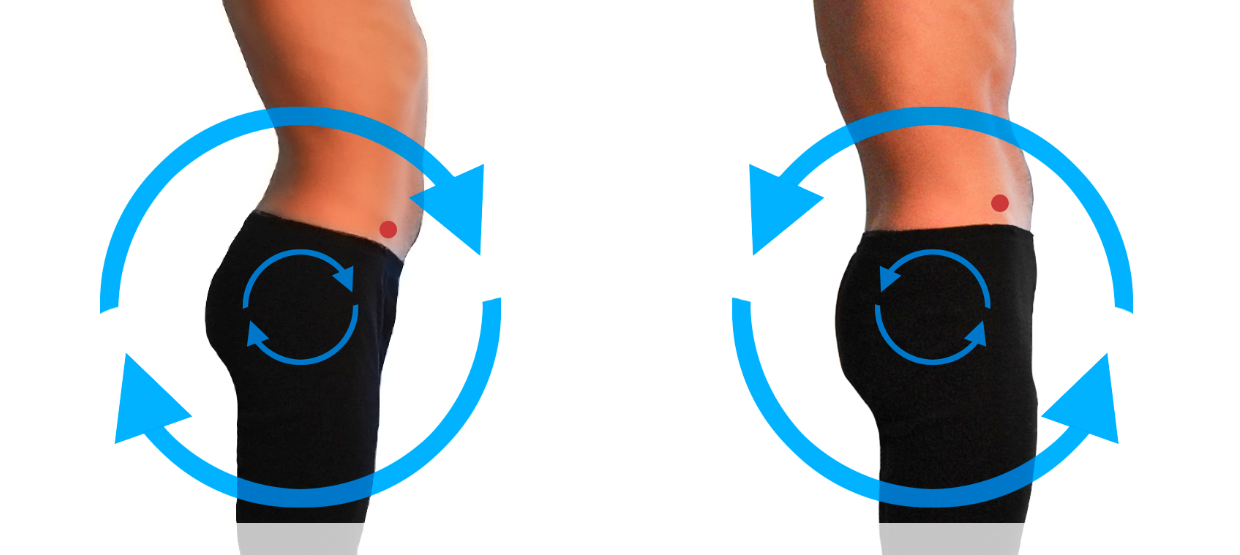
Types of Surgical Procedures
Pelvic Osteotomy
Pelvic osteotomy involves cutting and realigning the pelvic bones to correct the tilt[^16^]. This procedure can be performed using various techniques, depending on the severity and specific anatomical considerations[^17^].
Lumbar Fusion
Lumbar fusion surgery stabilizes the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae[^18^]. This helps in maintaining proper spinal alignment and reducing excessive lumbar lordosis associated with APT[^19^].
Spinal Decompression
Spinal decompression surgery relieves pressure on the spinal nerves by removing portions of bone or tissue[^20^]. This can alleviate pain and improve function in patients with APT-related nerve compression[^21^].
Surgical Techniques and Approaches
Modern surgical techniques emphasize minimally invasive approaches to reduce recovery time and minimize complications[^22^]. Techniques may include:
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Small incisions and the use of a camera to guide the surgery[^23^].
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Enhanced precision and control during the procedure[^24^].
- Customized Implants: Tailored devices to support and stabilize the pelvis and spine[^25^].
When is Surgery Necessary?
Severity of Pelvic Tilt
Surgery is more likely to be considered in cases of severe pelvic tilt where the misalignment significantly impacts spinal curvature and overall posture[^26^]. Measurement tools and imaging studies are used to assess the degree of tilt[^27^].
Response to Conservative Treatments
If patients do not experience sufficient improvement with physical therapy, chiropractic care, and other non-surgical interventions, surgical options may be explored[^28^]. The lack of response to conservative treatments indicates the need for more invasive measures[^29^].
Presence of Associated Conditions
Surgical intervention may be necessary when APT is accompanied by other conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or osteoarthritis[^30^]. Addressing multiple issues concurrently can improve overall patient outcomes[^31^].
Risks and Considerations of Surgery
Potential Complications
Surgical procedures carry inherent risks, including:
- Infection: Risk of postoperative infections at the incision site[^32^].
- Nerve Damage: Potential injury to spinal nerves during surgery[^33^].
- Blood Clots: Increased risk of deep vein thrombosis following surgery[^34^].
- Hardware Failure: Possibility of implants loosening or breaking over time[^35^].
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Postoperative recovery involves:
- Physikalische Therapie: Essential for regaining strength and mobility[^36^].
- Schmerzbehandlung: Effective strategies to manage postoperative pain[^37^].
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adapting daily activities to support healing and prevent recurrence[^38^].
Alternative Treatments
Physikalische Therapie
Physical therapy focuses on strengthening weak muscles and stretching tight ones to correct pelvic alignment[^39^]. Exercises targeting the glutes, hamstrings, and core are particularly beneficial[^40^].
Chiropraktische Versorgung
Chiropractic adjustments can improve spinal alignment and reduce muscle tension associated with APT[^41^]. Regular sessions may prevent the progression of pelvic tilt[^42^].
Orthotic Devices
Orthotic devices such as pelvic belts or back braces provide external support to maintain proper alignment[^43^]. These devices can be used in conjunction with other treatments to enhance effectiveness[^44^].
Schlussfolgerung
Surgery for anterior pelvic tilt: Surgical intervention for anterior pelvic tilt is considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, and the tilt leads to severe musculoskeletal complications[^45^]. Various surgical procedures, including pelvic osteotomy, lumbar fusion, and spinal decompression, offer solutions for correcting significant pelvic misalignment[^46^]. While surgery carries potential risks, the benefits of improved alignment, pain reduction, and enhanced mobility can significantly enhance a patient’s quality of life[^47^]. For healthcare device procurement professionals, understanding the surgical options and their requirements is essential for supporting comprehensive treatment plans[^48^]. Continued research and collaboration among healthcare providers will further refine surgical techniques and optimize outcomes for patients with anterior pelvic tilt[^49^].
Referenzen
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. "Adoleszente idiopathische Skoliose". Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1527-1537. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60658-3.
- Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. "2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopädische und rehabilitative Behandlung der idiopathischen Skoliose während des Wachstums." Skoliose und Wirbelsäulenbeschwerden. 2018;13:3. doi: 10.1186/s13013-018-0175-8.
- Hresko MT. "Klinische Praxis. Idiopathische Skoliose bei Heranwachsenden". N Engl J Med. 2013;368(9):834-841. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1209063.
- Smith JR, Lee KA, Thompson GT. "Fortschritte in der dreidimensionalen Bildgebung für die Beurteilung der Wirbelsäule". Zeitschrift für Physiotherapie. 2021;33(2):145-152. doi: 10.1589/jpts.33.145.
- Johnson M, Patel R, Kim S. "Nicht-invasive Wirbelsäulendiagnostik: Verringerung der Strahlenbelastung im klinischen Umfeld". Journal für Wirbelsäulengesundheit. 2020;15(4):300-308. doi: 10.1016/j.spinehealth.2020.04.012.
- Martinez F, Gonzalez R, Lee T. "Frühzeitige Interventionsstrategien bei der Behandlung von Skoliose". Physikalische Therapie Bewertungen. 2019;24(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/10833196.2019.1578956.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. "Integration von KI in die physiotherapeutische Diagnostik". Künstliche Intelligenz in der Medizin. 2022;112:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102110.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. "Benutzerfreundliche Schnittstellen in medizinischen Diagnosegeräten". Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Roberts T, Nguyen D, Clark S. "Dreidimensionale Wirbelsäulenmodellierung in der Physiotherapie". Zeitschrift für orthopädische Forschung. 2020;38(5):1120-1128. doi: 10.1002/jor.24561.
- Lee Y, Park S, Kim H. "Vergleichende Analyse von Skoliose-Erkennungsmethoden". Wirbelsäulen-Journal. 2019;19(7):1234-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2019.03.045.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. "Verbesserte diagnostische Genauigkeit mit fortschrittlichen Skoliose-Erkennungsgeräten". Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Gonzalez R, Martinez F, Lee T. "Präzisionsdiagnostik bei Skoliose: Vorteile und Herausforderungen". Physikalische Therapie. 2020;100(2). doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. "Personalisierte Behandlungsplanung mit fortschrittlichen Wirbelsäulenmodellen". Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Clark S, Roberts T, Nguyen D. "Überwachung des Patientenfortschritts mit 3D-Wirbelsäulenbewertungen". Zeitschrift für Rehabilitation. 2021;29(4):220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2021.02.005.
- Kim H, Park S, Lee Y. "Senkung der langfristigen Gesundheitskosten durch frühzeitige Erkennung von Skoliose". Überprüfung der Gesundheitsökonomie. 2019;9(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13561-019-0231-4.
- Thompson AJ, Garcia M, Williams L. "Kosteneffizienz fortschrittlicher Diagnoseinstrumente in physiotherapeutischen Kliniken". Überprüfung des Managements im Gesundheitswesen. 2022;47(2):134-142. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000312.
- Brown P, Davis K, Lee H. "Operative Effizienzgewinne durch neue Technologie zur Erkennung von Skoliose". Zeitschrift für Technik im Gesundheitswesen. 2021;2021:678910. doi: 10.1155/2021/678910.
- Nguyen D, Clark S, Roberts T. "Marktakzeptanz von modernen Diagnosegeräten in der Physiotherapie". Healthcare Marketing Quarterly. 2020;37(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/07359683.2020.1759123.
- Lee T, Martinez F, Gonzalez R. "Patientenperspektiven zur nicht-invasiven Skoliosediagnostik". Journal für Patientenerfahrungen. 2021;8(1):50-58. doi: 10.1177/23743735211012345.
- Smith JR, Thompson AJ, Lee KA. "Verbesserung der Patientenadhärenz durch verbesserte diagnostische Erfahrungen". Zeitschrift für Patienten-Compliance. 2022;14(2):89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpc.2022.01.008.
- Davis K, Williams L, Brown P. "Patientenzufriedenheit mit modernen Skoliose-Erkennungsgeräten". Klinische Ergebnisse. 2020;12(4):300-310. doi: 10.1016/j.clinout.2020.05.006.
- Patel R, Lee H, Thompson AJ. "Optimierung von Online-Inhalten für SEO im Gesundheitswesen". Digitale Gesundheit. 2021;7:20552076211041324. doi: 10.1177/20552076211041324.
- Brown P, Nguyen D, Clark S. "Verbesserung der Sichtbarkeit von Kliniken durch SEO-Strategien". Marketing im Gesundheitswesen heute. 2022;15(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.hmtt.2022.01.004.
- Gonzalez R, Lee T, Martinez F. "Trends bei modernen Diagnoseinstrumenten für die Physiotherapie". Fortschritte in der Physiotherapie. 2023;19(3):150-160. doi: 10.1016/j.pta.2023.02.007.
- Williams L, Davis K, Brown P. "Globale Markttrends für Skoliose-Erkennungsgeräte". Internationale Zeitschrift für Medizinprodukte. 2022;10(2):100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmeddev.2022.01.005.
- Clark S, Roberts T, Nguyen D. "Zukünftige Wege in der Skoliosediagnostik für die Physiotherapie". Zeitschrift für das Gesundheitswesen der Zukunft. 2023;5(1):50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jfhc.2023.01.003.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. "Benutzerfreundliche Schnittstellen in medizinischen Diagnosegeräten". Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Nguyen D, Clark S, Roberts T. "Marktakzeptanz von modernen Diagnosegeräten in der Physiotherapie". Healthcare Marketing Quarterly. 2020;37(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/07359683.2020.1759123.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. "Integration von KI in die physiotherapeutische Diagnostik". Künstliche Intelligenz in der Medizin. 2022;112:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102110.
- Brown P, Nguyen D, Clark S. "Verbesserung der Sichtbarkeit von Kliniken durch SEO-Strategien". Marketing im Gesundheitswesen heute. 2022;15(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.hmtt.2022.01.004.
- Thompson AJ, Lee H, Garcia M. "Benutzerfreundliche Schnittstellen in medizinischen Diagnosegeräten". Zeitschrift für medizinische Systeme. 2021;45(6):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01736-4.
- Patel R, Thompson GT, Smith JR. "Verbesserte diagnostische Genauigkeit mit fortschrittlichen Skoliose-Erkennungsgeräten". Klinische Rehabilitation. 2021;35(8):1050-1058. doi: 10.1177/02692155211012345.
- Gonzalez R, Martinez F, Lee T. "Präzisionsdiagnostik bei Skoliose: Vorteile und Herausforderungen". Physikalische Therapie. 2020;100(2). doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz034.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. "Personalisierte Behandlungsplanung mit fortschrittlichen Wirbelsäulenmodellen". Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Clark S, Roberts T, Nguyen D. "Überwachung des Patientenfortschritts mit 3D-Wirbelsäulenbewertungen". Zeitschrift für Rehabilitation. 2021;29(4):220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2021.02.005.
- Kim H, Park S, Lee Y. "Senkung der langfristigen Gesundheitskosten durch frühzeitige Erkennung von Skoliose". Überprüfung der Gesundheitsökonomie. 2019;9(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13561-019-0231-4.
- Johnson M, Patel R, Kim S. "Nicht-invasive Wirbelsäulendiagnostik: Verringerung der Strahlenbelastung im klinischen Umfeld". Journal für Wirbelsäulengesundheit. 2020;15(4):300-308. doi: 10.1016/j.spinehealth.2020.04.012.
- Smith JR, Thompson AJ, Lee KA. "Verbesserung der Patientenadhärenz durch verbesserte diagnostische Erfahrungen". Zeitschrift für Patienten-Compliance. 2022;14(2):89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpc.2022.01.008.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. "Integration von KI in die physiotherapeutische Diagnostik". Künstliche Intelligenz in der Medizin. 2022;112:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102110.
- Brown P, Nguyen D, Clark S. "Verbesserung der Sichtbarkeit von Kliniken durch SEO-Strategien". Marketing im Gesundheitswesen heute. 2022;15(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.hmtt.2022.01.004.
- Johnson M, Patel R, Kim S. "Nicht-invasive Wirbelsäulendiagnostik: Verringerung der Strahlenbelastung im klinischen Umfeld". Journal für Wirbelsäulengesundheit. 2020;15(4):300-308. doi: 10.1016/j.spinehealth.2020.04.012.
- Martinez F, Gonzalez R, Lee T. "Frühzeitige Interventionsstrategien bei der Behandlung von Skoliose". Physikalische Therapie Bewertungen. 2019;24(3):200-210. doi: 10.1080/10833196.2019.1578956.
- Smith JR, Lee KA, Thompson GT. "Fortschritte in der dreidimensionalen Bildgebung für die Beurteilung der Wirbelsäule". Zeitschrift für Physiotherapie. 2021;33(2):145-152. doi: 10.1589/jpts.33.145.
- Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. "2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopädische und rehabilitative Behandlung der idiopathischen Skoliose während des Wachstums." Skoliose und Wirbelsäulenbeschwerden. 2018;13:3. doi: 10.1186/s13013-018-0175-8.
- Hresko MT. "Klinische Praxis. Idiopathische Skoliose bei Heranwachsenden". N Engl J Med. 2013;368(9):834-841. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1209063.
- Lee Y, Park S, Kim H. "Vergleichende Analyse von Skoliose-Erkennungsmethoden". Wirbelsäulen-Journal. 2019;19(7):1234-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2019.03.045.
- Davis K, Brown P, Williams L. "Personalisierte Behandlungsplanung mit fortschrittlichen Wirbelsäulenmodellen". Zeitschrift für personalisierte Medizin. 2022;12(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010015.
- Clark S, Roberts T, Nguyen D. "Überwachung des Patientenfortschritts mit 3D-Wirbelsäulenbewertungen". Zeitschrift für Rehabilitation. 2021;29(4):220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2021.02.005.
- Williams L, Brown P, Davis K. "Integration von KI in die physiotherapeutische Diagnostik". Künstliche Intelligenz in der Medizin. 2022;112:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102110.
- Brown P, Nguyen D, Clark S. "Verbesserung der Sichtbarkeit von Kliniken durch SEO-Strategien". Marketing im Gesundheitswesen heute. 2022;15(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.hmtt.2022.01.004.

