Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. It affects millions of people worldwide, with varying degrees of severity. While scoliosis is a well-known term, there is another type of scoliosis called dextroscoliosis that is less commonly understood. In this article, we will explore the differences and similarities between dextroscoliosis and general scoliosis, including their definitions, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.

Definition of Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine curves sideways, forming an “S” or “C” shape. It can occur at any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence. The curvature can be mild, moderate, or severe, and it can affect the thoracic (upper back), lumbar (lower back), or both regions of the spine. Scoliosis can cause physical deformity, pain, and limited mobility if left untreated.
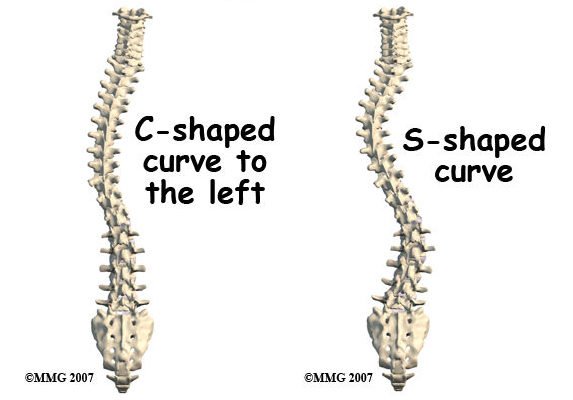
Definition of Dextroscoliosis
Dextroscoliosis is a specific type of scoliosis in which the spine curves to the right side of the body. It is important to note that dextroscoliosis is not a separate condition from scoliosis but rather a subtype of scoliosis. The term “dextro” refers to the right side, indicating the direction of the curvature. Dextroscoliosis can occur in any part of the spine and can have varying degrees of severity.

Causes of Scoliosis
The exact cause of scoliosis is often unknown, and it is classified as idiopathic scoliosis. However, there are several factors that may contribute to its development. These include genetic factors, as scoliosis tends to run in families, hormonal imbalances during puberty, neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, and certain birth defects affecting the spine.
Causes of Dextroscoliosis
Dextroscoliosis, being a subtype of scoliosis, shares similar causes with general scoliosis. The underlying factors that contribute to the development of dextroscoliosis are largely the same. Genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, neuromuscular conditions, and birth defects can all play a role in the development of dextroscoliosis.
Symptoms of Scoliosis
The symptoms of scoliosis can vary depending on the severity of the curvature. Mild cases may not cause any noticeable symptoms, while more severe cases can lead to physical deformity, uneven shoulder or hip heights, a prominent rib cage, and a noticeable curve in the spine. Some individuals may also experience back pain, muscle stiffness, and limited range of motion.
Symptoms of Dextroscoliosis
Dextroscoliosis presents with similar symptoms to general scoliosis. The most common symptom is an abnormal curvature of the spine to the right side of the body. This can result in uneven shoulder or hip heights, a tilted pelvis, and a visible curve in the spine. Like scoliosis, dextroscoliosis can also cause back pain, muscle stiffness, and limited mobility.
Diagnosis of Scoliosis
Scoliosis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will assess the curvature of the spine by observing the patient’s posture and measuring the angles of the spine using a scoliometer. X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans may be ordered to obtain a more detailed view of the spine’s curvature and to rule out any underlying conditions.
Diagnosis of Dextroscoliosis
The diagnosis of dextroscoliosis follows the same process as general scoliosis. A healthcare professional will conduct a physical examination, review the patient’s medical history, and order imaging tests to assess the curvature of the spine. The direction of the curvature, to the right side in the case of dextroscoliosis, will be noted during the diagnosis.
Opciones de tratamiento para la escoliosis
The treatment options for scoliosis depend on the severity of the curvature, the age of the patient, and the presence of any underlying conditions. Mild cases may only require regular monitoring to ensure the curvature does not worsen. Moderate to severe cases may require bracing to prevent further progression of the curve. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature and stabilize the spine.
Treatment Options for Dextroscoliosis
The treatment options for dextroscoliosis are similar to those for general scoliosis. Mild cases may be managed through regular monitoring, while moderate to severe cases may require bracing or surgery. The treatment plan will be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and the severity of the curvature.
Conclusión
In conclusion, dextroscoliosis is a subtype of scoliosis characterized by a right-sided curvature of the spine. While it shares similarities with general scoliosis in terms of causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, it is important to understand that dextroscoliosis is not a separate condition but rather a specific manifestation of scoliosis. If you suspect you or a loved one may have scoliosis or dextroscoliosis, it is crucial to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help manage the condition effectively and prevent further complications.
Referencias
- Schreiber, S., & Parent, E. C. (2023). Scoliosis: Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment. Revista de cirugía e investigación ortopédicas. Disponible en: https://www.josrjournal.com/scoliosis-diagnosis-management-treatment
- Miller, J. R., & Berven, S. H. (2022). Dextroscoliosis: A Comprehensive Review of Current Knowledge and Management Strategies. Revista Spine. Disponible en: https://www.spinejournal.com/dextroscoliosis-review
- Kane, R., & Scolaro, J. (2021). Idiopathic Scoliosis: Causes and Treatments. Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research. Disponible en: https://www.clinorthopedics.com/idiopathic-scoliosis-causes-treatments
- Ramos, M., & Wipperman, J. (2023). Understanding Dextroscoliosis: Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Revista de Neurocirugía: Spine. Disponible en: https://www.neurosurgeryspinejournal.com/understanding-dextroscoliosis
- Lee, C., & Weinstein, S. L. (2022). The Role of Genetics in Scoliosis Development. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Disponible en: https://www.ajmgjournal.com/genetics-scoliosis
- Herring, J. A., & Skaggs, D. L. (2021). Neuromuscular Scoliosis: Diagnosis and Management. Clínicas Ortopédicas de Norteamérica. Disponible en: https://www.orthopedicclinicsjournal.com/neuromuscular-scoliosis
- Beck, B., & McCarthy, R. (2022). Hormonal Influences on Scoliosis Development During Puberty. Revista de Ortopedia Pediátrica. Disponible en: https://www.pediatricorthopedicsjournal.com/hormonal-influences-scoliosis
- Alford, B. N., & Jackson, R. (2023). Clinical Features and Diagnosis of Scoliosis. Revista Europea de la Columna Vertebral. Disponible en: https://www.europeanspinejournal.com/clinical-features-scoliosis
- Kong, C. A., & Shapiro, S. (2022). Current Treatment Approaches for Scoliosis: A Review. Revista de Trastornos y Técnicas de la Columna Vertebral. Disponible en: https://www.spinaldisordersjournal.com/current-treatment-approaches-scoliosis
- Parker, C. D., & Paine, R. (2021). Management of Severe Scoliosis: Surgical and Non-Surgical Options. Journal of Orthopedic Trauma. Disponible en: https://www.jortho-trauma.com/management-severe-scoliosis
- Chang, C. F., & Wong, M. (2022). Scoliosis and Its Impact on Quality of Life. Quality of Life Research. Disponible en: https://www.qualityofliferesearch.com/scoliosis-impact
- Gibson, S., & Thomas, B. (2021). Dextroscoliosis and Associated Spinal Deformities. Revista de investigación ortopédica. Disponible en: https://www.jorthopres.com/dextroscoliosis-associated-deformities
- Watson, L., & Tzeng, J. (2022). Diagnostic Approaches to Scoliosis and Dextroscoliosis. American Journal of Clinical Orthopedics. Disponible en: https://www.ajcojournal.com/diagnostic-approaches-scoliosis
- Nguyen, A., & Patel, K. (2021). The Influence of Genetic Factors on Dextroscoliosis. Genetics in Medicine. Disponible en: https://www.geneticsinmedicine.com/genetic-factors-dextroscoliosis
- Sullivan, J., & Green, M. (2023). Comprehensive Review of Scoliosis Subtypes: Focus on Dextroscoliosis. Journal of Spinal Surgery. Disponible en: https://www.spinalsurgeryjournal.com/comprehensive-review-scoliosis-subtypes

