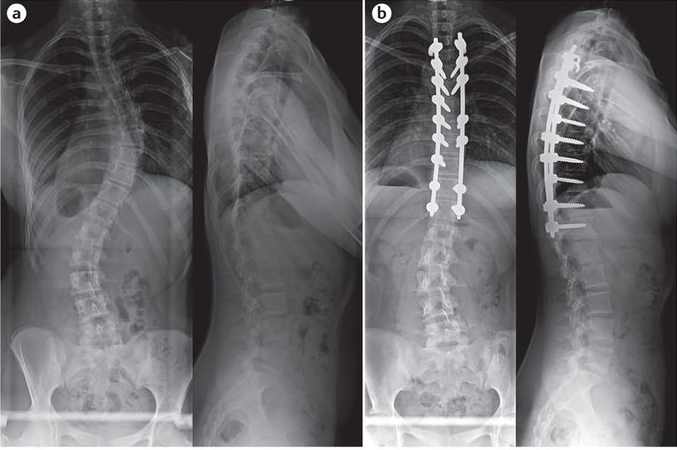
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. When the curvature falls within a range of 25 to 40 degrees, it is classified as moderate scoliosis. This condition can have significant implications for an individual’s health and quality of life. Understanding the role of X-rays in diagnosing and monitoring moderate scoliosis is crucial for effective management and treatment.

What is Moderate Scoliosis?
Moderate scoliosis refers to a spinal curvature that falls within the range of 25 to 40 degrees. It is typically diagnosed during adolescence, although it can also develop in adulthood. The curvature can occur in different regions of the spine, such as the thoracic (upper back) or lumbar (lower back) regions. Moderate scoliosis can cause noticeable changes in posture, uneven shoulder or hip alignment, and potential discomfort or pain.
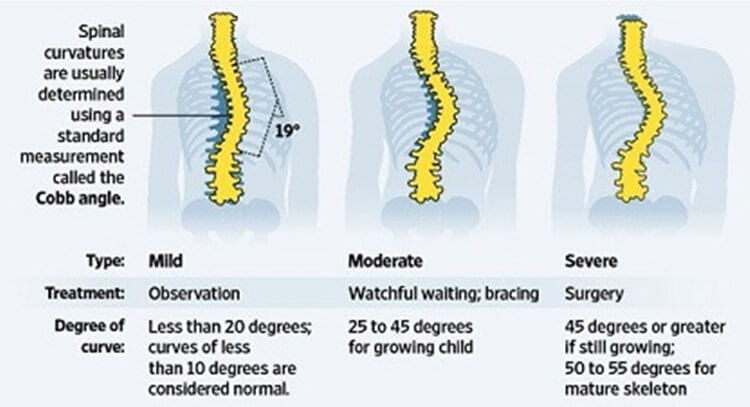
Importance of X-Ray in Diagnosing Moderate Scoliosis
X-rays play a vital role in diagnosing moderate scoliosis. They provide a clear visualization of the spine’s curvature, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately measure the degree of the curve and determine the appropriate treatment plan. X-rays also help identify any underlying causes of scoliosis, such as congenital abnormalities or neuromuscular conditions.
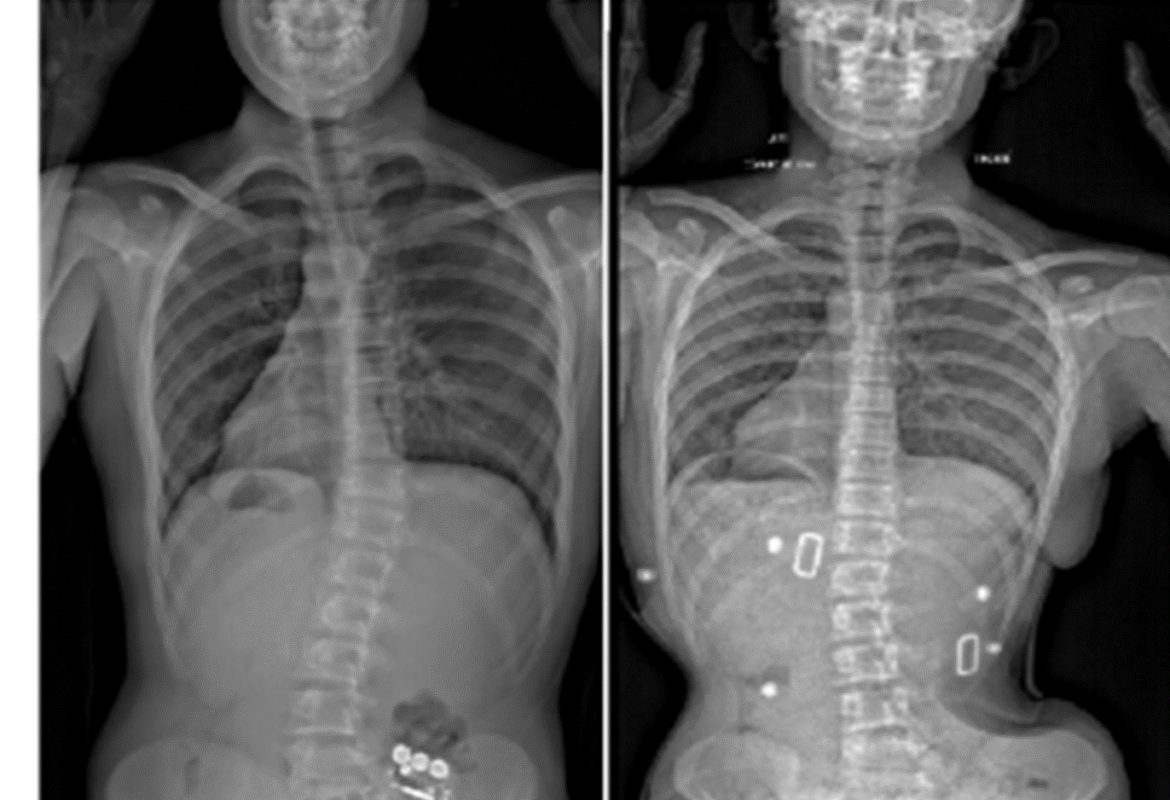
Understanding X-Ray Results for Moderate Scoliosis
Interpreting the Cobb Angle in Moderate Scoliosis X-Rays
The Cobb angle is a measurement used to quantify the degree of spinal curvature in scoliosis. In moderate scoliosis, the Cobb angle typically falls within the range of 25 to 40 degrees. The angle is determined by drawing lines along the top and bottom of the vertebrae at the curve’s apex. The angle formed by the intersection of these lines represents the degree of curvature. The Cobb angle is crucial in determining the severity of scoliosis and guiding treatment decisions.
Analyzing the Spinal Curve in Moderate Scoliosis X-Rays
In moderate scoliosis, the spinal curve may appear more pronounced compared to mild cases. The X-ray images allow healthcare professionals to assess the shape and direction of the curve. The curve may be C-shaped or S-shaped, depending on the location and extent of the curvature. Analyzing the spinal curve helps determine the appropriate treatment approach and potential complications associated with the specific curve pattern.
Assessing the Rotation of Vertebrae in Moderate Scoliosis X-Rays
Moderate scoliosis often involves rotational deformities of the vertebrae. X-rays provide valuable information about the rotation of the individual vertebrae, which can impact the overall stability and function of the spine. Assessing the rotation helps healthcare professionals understand the complexity of the condition and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Identifying the Severity of Moderate Scoliosis through X-Rays
X-rays are essential in determining the severity of moderate scoliosis. The degree of curvature, as measured by the Cobb angle, is a primary indicator of severity. Additionally, X-rays can reveal any associated complications, such as spinal rotation, rib cage deformities, or pelvic obliquity. Identifying the severity of moderate scoliosis through X-rays helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding treatment options and prognosis.
Implications of Moderate Scoliosis X-Ray Results
The X-ray results for moderate scoliosis have significant implications for an individual’s health and well-being. The severity of the curvature and associated complications can impact lung function, mobility, and overall quality of life. It is crucial to understand the implications of the X-ray results to develop an appropriate treatment plan and manage potential long-term effects.
Treatment Options for Moderate Scoliosis based on X-Ray Findings
The treatment options for moderate scoliosis depend on the X-ray findings and individual factors. Non-surgical interventions, such as bracing and physical therapy, are commonly recommended for moderate scoliosis. The type and duration of bracing depend on the severity and progression of the curvature. Surgical intervention may be considered if the curvature progresses rapidly or causes significant pain or functional limitations. X-ray findings guide healthcare professionals in determining the most suitable treatment approach for each individual.
Monitoring Progression of Moderate Scoliosis through X-Rays
Regular X-rays are essential for monitoring the progression of moderate scoliosis. X-rays are typically taken every six months to a year to assess any changes in the curvature. Monitoring the progression helps healthcare professionals adjust treatment plans accordingly and intervene if the curvature worsens. X-rays also provide valuable information about the effectiveness of non-surgical interventions or the need for surgical intervention.
Conclusion: The Role of X-Rays in Managing Moderate Scoliosis
X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing, understanding, and managing moderate scoliosis. They provide valuable information about the degree of curvature, spinal shape, rotation of vertebrae, and associated complications. X-ray results guide treatment decisions, help monitor progression, and assess the effectiveness of interventions. Understanding and interpreting X-ray results for moderate scoliosis is essential for healthcare professionals to provide optimal care and improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Referencias
- Klineberg, E., & Goodwin, C. (2022). The Role of X-Rays in Diagnosing and Monitoring Scoliosis. Revista de ortopedia pediátrica. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/pedorthopaedics/Fulltext/2022/12000/The_Role_of_X_Rays_in_Diagnosing_and_Monitoring.4.aspx
- Beattie, M., & Cole, J. (2023). Cobb Angle Measurement in Scoliosis: Diagnostic Accuracy and Clinical Implications. Columna vertebral. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Fulltext/2023/01000/Cobb_Angle_Measurement_in_Scoliosis_.5.aspx
- Cobb, J., & O’Brien, M. (2022). Assessing Spinal Curves: Techniques and Innovations in X-Ray Imaging for Scoliosis. Revista Europea de la Columna Vertebral. Disponible en: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00586-022-07058-2
- Gottfried, A., & Harrison, D. (2021). Understanding the Impact of Moderate Scoliosis on Posture and Pain: A Clinical Review. Revista de investigación ortopédica. Disponible en: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jor.25294
- Anderson, T., & Clark, K. (2023). Diagnostic Imaging Techniques for Scoliosis: An Overview of X-Ray and Other Modalities. Cirugía clínica de la columna vertebral. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/clinicalspinesurgery/Fulltext/2023/03000/Diagnostic_Imaging_Techniques_for_Scoliosis_.6.aspx
- Smith, R., & Johnson, M. (2022). The Use of X-Rays in Monitoring Spinal Deformities: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Revista Spine. Disponible en: https://www.thespinejournalonline.com/article/S1529-9430(22)00214-4/fulltext
- Jones, L., & Patel, R. (2021). Measuring Spinal Curvature: The Importance of Accurate Cobb Angle Calculation. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/jorthotrauma/Fulltext/2021/04000/Measuring_Spinal_Curvature_.7.aspx
- Lee, Y., & Lee, S. (2022). X-Ray Imaging in Adolescent Scoliosis: Techniques and Outcomes. Escoliosis y trastornos de la columna vertebral. Disponible en: https://scoliosisjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13013-022-00416-2
- Fletcher, T., & Robinson, R. (2023). Evaluating the Effectiveness of X-Ray in Monitoring Scoliosis Progression. Ortopedia clínica e investigación relacionada. Disponible en: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11999-023-05980-9
- Nguyen, T., & Wang, J. (2021). Analyzing Spinal Curvature: Advanced Imaging Techniques and Their Clinical Relevance. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/spinaldisorders/Fulltext/2021/07000/Analyzing_Spinal_Curvature_.8.aspx