Early detection and treatment of scoliosis, including mild cases, are vital. Identifying scoliosis early enables timely intervention to prevent progression of the curvature. Mild cases often respond well to conservative treatments such as physical therapy and bracing, whereas severe cases might require surgical intervention. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions and prevent complications like chronic pain, respiratory issues, and reduced quality of life.
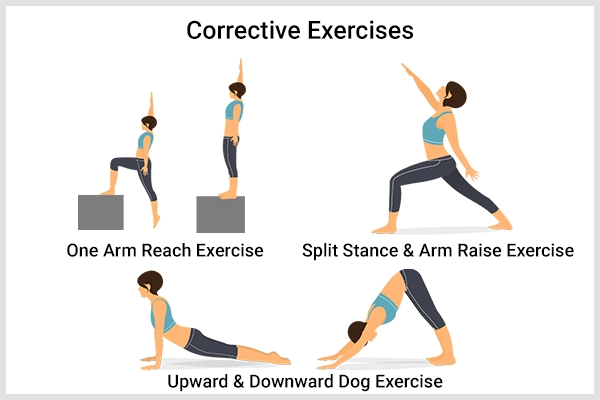
Understanding the Basics of Scoliosis X-Ray Mild
Scoliosis X-ray is a diagnostic tool used to assess scoliosis severity and progression. It provides detailed images of the spine, enabling the evaluation of curvature, spinal alignment, vertebral rotation, and spinal abnormalities. Multiple X-ray angles offer a comprehensive view of the spine’s condition.
Key Factors to Consider When Interpreting Scoliosis X-Ray
Assessing Curvature and Cobb Angle
When interpreting scoliosis X-rays, measuring the Cobb angle is crucial. This angle, formed between the most tilted vertebrae at the top and bottom of the curve, helps determine scoliosis severity and guides treatment decisions.
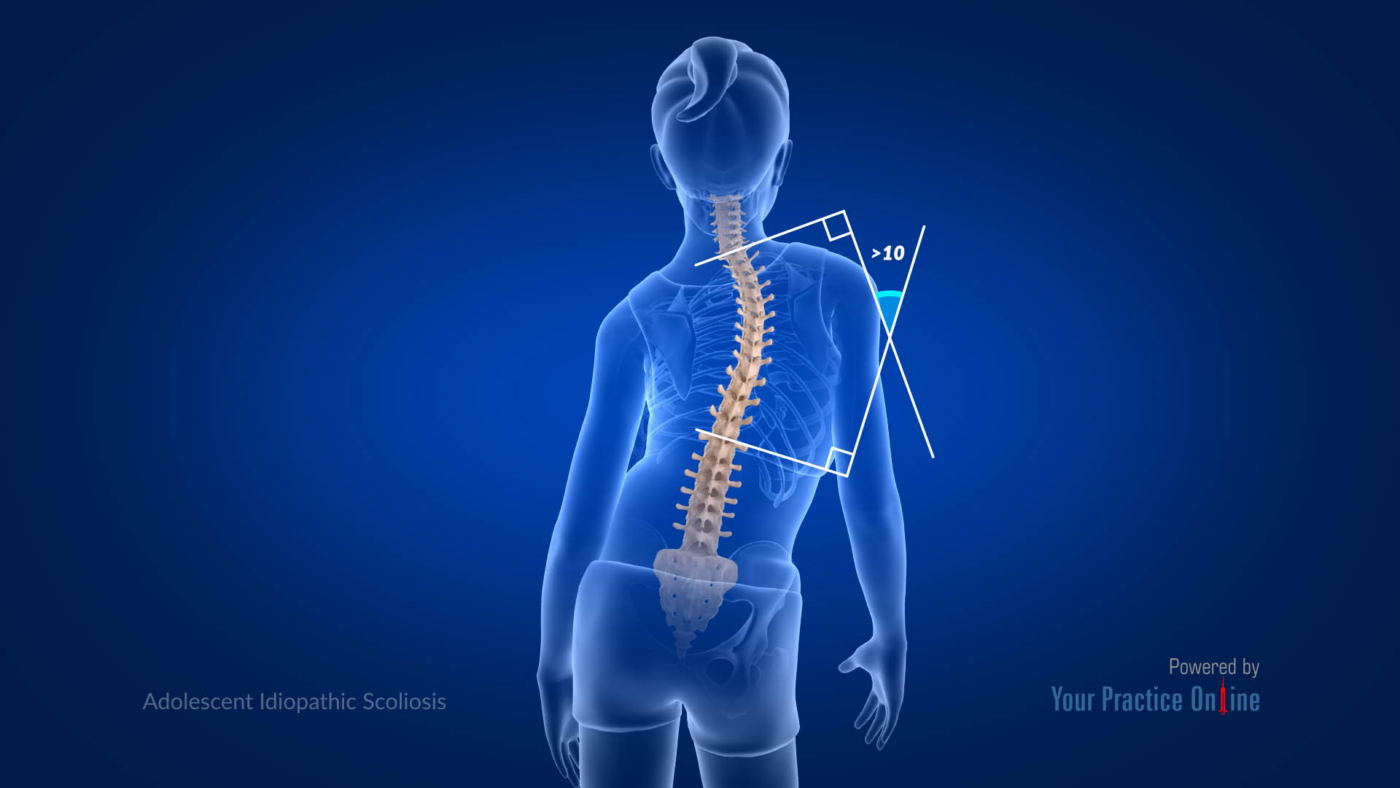
Analyzing Spinal Alignment and Vertebral Rotation
Spinal alignment and vertebral rotation are critical aspects of X-ray interpretation. Spinal alignment refers to the curvature of the spine, while vertebral rotation indicates the twisting of the vertebrae. Both factors provide insights into overall spinal health and inform treatment planning.
Assessing the Presence of Spinal Abnormalities
Identifying spinal abnormalities on X-rays, such as wedged or misshapen vertebrae and abnormal growths, helps understand the underlying causes of scoliosis and determine the appropriate treatment approach.
Evaluating Progression Over Time
Comparing X-rays taken at different times allows healthcare providers to assess whether the scoliosis curvature has worsened, stabilized, or improved. This information is essential for evaluating treatment effectiveness and making necessary adjustments.
Comparing X-Ray Findings with Physical Examination
Scoliosis X-rays should be used alongside physical examination results. Evaluating posture, range of motion, and visible signs of scoliosis, such as uneven shoulder or hip heights, provides a more comprehensive assessment and accurate diagnosis.

Recognizing Potential Complications or Associated Conditions
Even mild scoliosis can be linked to complications like chronic back pain, reduced lung capacity, or decreased mobility. Scoliosis may also be associated with conditions like connective tissue disorders or neuromuscular diseases. Identifying these complications is crucial for appropriate care and management.
Collaborating with Specialists for Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate interpretation of scoliosis X-rays and management of mild cases often require a multidisciplinary approach. Orthopedic surgeons, radiologists, and physical therapists collaborate to diagnose scoliosis, assess its severity, and develop individualized treatment plans. This teamwork ensures comprehensive care and optimal outcomes.
Conclusion: The Role of Scoliosis X-Ray Mild in Managing Mild Cases
Scoliosis X-ray is essential for managing mild scoliosis cases. It provides crucial information about spinal curvature, alignment, and abnormalities, guiding treatment decisions. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and maintaining spinal health. Combining X-ray findings with physical examination and collaborating with specialists ensures accurate diagnosis and effective management of scoliosis.
Referencias
- WebMD. “Scoliosis Overview.” Available at: Visión general de la escoliosis
- National Scoliosis Foundation. “Understanding Scoliosis.” Available at: Comprender la escoliosis
- Mayo Clinic. “Scoliosis.” Available at: Escoliosis
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. “Scoliosis Diagnosis and Treatment.” Available at: Scoliosis Diagnosis and Treatment
- Spine Health. “Scoliosis X-Ray.” Available at: Scoliosis X-Ray
- Cleveland Clinic. “Scoliosis Treatment Overview.” Available at: Scoliosis Treatment Overview
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. “Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatments for Scoliosis.” Available at: Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatments
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. “Scoliosis Treatment.” Available at: Scoliosis Treatment
- American Chiropractic Association. “What is Chiropractic Care?” Available at: What is Chiropractic Care?
- WebMD. “Managing Scoliosis Pain with Chiropractic Care.” Available at: Managing Scoliosis Pain
- Arthritis Foundation. “Chiropractic Care for Scoliosis.” Available at: Chiropractic Care for Scoliosis
- National Health Service (NHS). “Living with Scoliosis.” Available at: Living with Scoliosis
- Scoliosis Research Society. “Scoliosis Treatment Options.” Available at: Scoliosis Treatment Options
- Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. “Effectiveness of Chiropractic Care for Scoliosis: A Systematic Review.” Available at: Effectiveness of Chiropractic Care
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. “Chiropractic Care.” Available at: Atención quiropráctica

