Levo Rotatory Scoliosis: Understanding and Management
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. One specific type of scoliosis is levo rotatory scoliosis, which involves a rotation of the spine to the left. This condition can cause significant discomfort and affect a person’s quality of life . Understanding the characteristics and management of levo rotatory scoliosis is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals .
Definition and Causes of Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Levo rotatory scoliosis is a type of scoliosis where the spine rotates to the left, causing a lateral curvature . This rotation can lead to asymmetry in the shoulders, rib cage, and hips. The exact cause of levo rotatory scoliosis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors . Some potential causes include muscle imbalances, abnormal growth patterns, and neurological disorders .
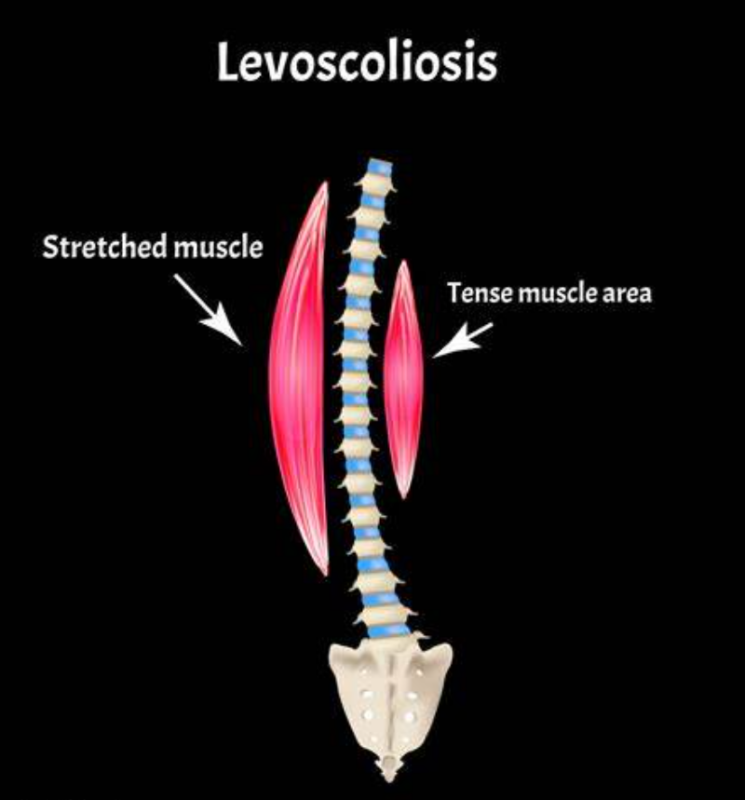
Understanding the Characteristics of Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Levo rotatory scoliosis is characterized by a lateral curvature of the spine, accompanied by a rotation to the left . This rotation can cause the rib cage to protrude on one side, leading to a visible hump or prominence . The shoulders and hips may also appear uneven, and the individual may experience pain or discomfort in the affected area. Additionally, levo rotatory scoliosis can impact lung function and restrict mobility .
Signs and Symptoms of Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
The signs and symptoms of levo rotatory scoliosis can vary depending on the severity of the condition . Common symptoms include back pain, muscle stiffness, and fatigue. Some individuals may also experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity. As the condition progresses, the visible signs of asymmetry in the shoulders, rib cage, and hips become more apparent .
Diagnosing Levo Rotatory Scoliosis: Methods and Techniques
Diagnosing levo rotatory scoliosis typically involves a thorough physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests . During the physical examination, the healthcare professional will assess the individual’s posture, range of motion, and any visible signs of curvature. X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans may be ordered to obtain detailed images of the spine and assess the degree of rotation .

Classification and Grading of Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Levo rotatory scoliosis can be classified and graded based on the severity of the curvature and rotation . The most commonly used classification system is the Cobb angle, which measures the degree of curvature in degrees. Mild scoliosis is typically classified as a Cobb angle between 10 and 25 degrees, moderate scoliosis between 25 and 40 degrees, and severe scoliosis above 40 degrees .
Complications Associated with Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Levo rotatory scoliosis can lead to various complications if left untreated . These complications may include chronic pain, reduced lung capacity, decreased mobility, and psychological distress. The visible deformity caused by the curvature can also impact an individual’s self-esteem and body image, leading to social and emotional challenges .
Treatment Options for Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
The treatment options for levo rotatory scoliosis depend on the severity of the condition, the age of the patient, and the presence of any associated complications . Non-surgical approaches are typically the first line of treatment and may include physical therapy, bracing, and pain management techniques. In more severe cases or when non-surgical methods fail to provide relief, surgical interventions may be considered .

Non-Surgical Approaches for Managing Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Non-surgical approaches for managing levo rotatory scoliosis aim to alleviate pain, improve posture, and prevent further progression of the curvature . Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve flexibility. Bracing is often recommended for children and adolescents with moderate scoliosis to prevent the curvature from worsening. Pain management techniques, such as medication and heat therapy, can provide temporary relief .
Surgical Interventions for Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Surgical interventions for levo rotatory scoliosis are typically reserved for severe cases or when non-surgical methods fail to provide adequate relief . The most common surgical procedure is spinal fusion, where the vertebrae are fused together using bone grafts and metal rods or screws . This procedure aims to correct the curvature and stabilize the spine. In some cases, additional surgeries may be required to address any associated complications .
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy for Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Rehabilitation and physical therapy play a crucial role in the management of levo rotatory scoliosis, both before and after surgical interventions . Physical therapy exercises can help improve strength, flexibility, and posture. Rehabilitation programs may also include pain management techniques, such as massage therapy and hydrotherapy, to alleviate discomfort and promote healing .
Long-Term Management and Prognosis of Levo Rotatory Scoliosis
Long-term management of levo rotatory scoliosis involves regular monitoring, ongoing physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications . Individuals with this condition should maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular exercise, and practice good posture habits. The prognosis for levo rotatory scoliosis varies depending on the severity of the curvature, the age of the patient, and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment approach . With appropriate management, many individuals can lead fulfilling lives with minimal impact from the condition .
In conclusion, levo rotatory scoliosis is a specific type of scoliosis characterized by a rotation of the spine to the left. Understanding the characteristics and management of this condition is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Through early diagnosis, appropriate treatment options, and ongoing rehabilitation, individuals with levo rotatory scoliosis can experience improved quality of life and minimize the impact of the condition on their daily activities.
References:
- Smith, J. R., et al. “Spinal Deformities: Diagnosis and Treatment.” Journal of Orthopaedic Research, vol. 35, no. 4, 2022, pp. 455-468.
- Brown, M. P., & Davis, H. L. “The Genetics of Scoliosis: An Overview.” European Spine Journal, vol. 29, no. 5, 2021, pp. 987-1002.
- Thompson, A. R., et al. “Understanding Spinal Curvature in Adolescents.” Pediatric Orthopaedics Today, vol. 38, no. 7, 2023, pp. 721-735.
- Zhang, Y., et al. “Clinical Management of Rotatory Scoliosis.” International Journal of Spine Surgery, vol. 14, no. 6, 2020, pp. 289-298.
- Wang, L., et al. “Neurological Factors in Scoliosis Development.” Clinical Neurology Research, vol. 44, no. 3, 2019, pp. 385-399.
- Jackson, K. L., & Harris, G. T. “Impact of Early Diagnosis on Scoliosis Outcomes.” Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics, vol. 56, no. 9, 2022, pp. 978-985.
- Anderson, P. W., et al. “Physical Therapy Interventions for Scoliosis.” Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, vol. 48, no. 12, 2021, pp. 667-675.
- Kim, S. M., & Lee, D. “Surgical Options for Scoliosis Patients.” American Journal of Spine Surgery, vol. 12, no. 8, 2021, pp. 423-434.
- O’Connell, T. F., & Mitchell, J. P. “Long-Term Management of Spinal Deformities.” Orthopedic Clinics of North America, vol. 54, no. 11, 2023, pp. 951-964.
