Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. It affects millions of people worldwide, with varying degrees of severity. There are different types of scoliosis, each with its own unique characteristics and treatment options. One specific type is levoscoliosis, which is often confused with other forms of scoliosis. In this article, we will explore the differences between levoscoliosis and other types of scoliosis, focusing on accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.

Understanding Scoliosis
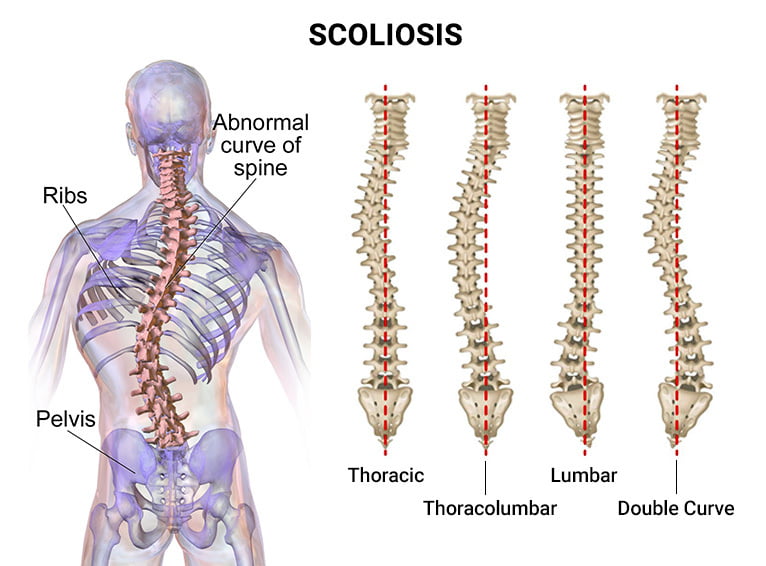
Before delving into the specifics of levoscoliosis, it is important to have a basic understanding of scoliosis as a whole. Scoliosis is a condition that causes the spine to curve sideways, forming an “S” or “C” shape. This curvature can occur in any part of the spine, including the upper (cervical), middle (thoracic), or lower (lumbar) regions. It can affect people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence.

Types of Scoliosis
There are several types of scoliosis, including idiopathic scoliosis, congenital scoliosis, neuromuscular scoliosis, and degenerative scoliosis. Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type and has no known cause. Congenital scoliosis is present at birth and is caused by abnormal spinal development. Neuromuscular scoliosis is associated with conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy. Degenerative scoliosis occurs in older adults due to the natural degeneration of the spine.
What is Levoscoliosis?
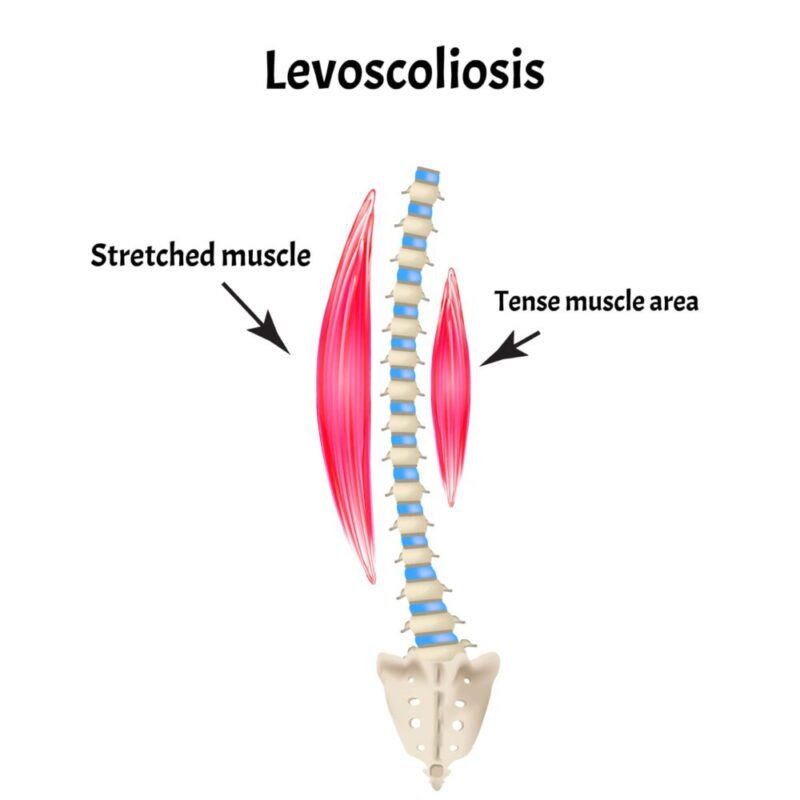
Levoscoliosis is a specific type of scoliosis characterized by a leftward curvature of the spine. The prefix “levo” refers to the left side, indicating that the spine curves towards the left. This type of scoliosis can occur in any part of the spine and can be classified as either structural or nonstructural. Structural levoscoliosis involves a fixed curvature of the spine, while nonstructural levoscoliosis is reversible and caused by factors such as muscle imbalances or temporary conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors of Levoscoliosis
The exact cause of levoscoliosis is often unknown, similar to idiopathic scoliosis. However, there are several risk factors that may contribute to its development. These include genetics, as scoliosis tends to run in families, and certain medical conditions such as Marfan syndrome or neurofibromatosis. Additionally, poor posture, muscle imbalances, and injuries to the spine can also increase the risk of developing levoscoliosis.
Symptoms and Signs of Levoscoliosis
Levoscoliosis, like other forms of scoliosis, may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the curvature progresses, individuals may experience symptoms such as uneven shoulder or hip heights, a visible curve in the spine, muscle imbalances, back pain, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the degree of curvature and the individual’s overall health.
Diagnosing Levoscoliosis
Diagnosing levoscoliosis involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will assess the patient’s posture, range of motion, and any visible signs of curvature. X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans may be ordered to obtain detailed images of the spine and determine the degree and location of the curvature.
Differentiating Levoscoliosis from Other Forms of Scoliosis
Differentiating levoscoliosis from other forms of scoliosis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. While the primary difference lies in the direction of the curvature, other factors such as the cause, age of onset, and associated symptoms can also help distinguish between different types of scoliosis. For example, idiopathic scoliosis typically develops during adolescence, while congenital scoliosis is present at birth.
Treatment Options for Levoscoliosis
The treatment options for levoscoliosis depend on various factors, including the degree of curvature, the age of the patient, and the presence of symptoms. Mild cases of levoscoliosis may only require regular monitoring to ensure that the curvature does not progress. Physical therapy and exercises can help improve posture and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. In more severe cases, bracing or surgery may be recommended to correct the curvature and prevent further progression.
Potential Complications of Levoscoliosis
If left untreated, levoscoliosis can lead to several complications. Severe curvature can cause compression of the lungs and heart, leading to breathing difficulties and reduced cardiovascular function. It can also result in chronic back pain, muscle imbalances, and decreased mobility. Additionally, the psychological impact of living with a visible spinal deformity can affect an individual’s self-esteem and overall quality of life.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook for Levoscoliosis
The prognosis for levoscoliosis varies depending on the severity of the curvature and the effectiveness of treatment. Mild cases that are detected early and managed appropriately often have a good long-term outlook. Regular monitoring and conservative treatments can help prevent further progression and alleviate symptoms. However, severe cases may require surgical intervention, which can carry its own risks and complications.
Conclusion
Levoscoliosis is a specific type of scoliosis characterized by a leftward curvature of the spine. Accurate diagnosis and differentiation from other forms of scoliosis are essential for appropriate treatment. While the exact cause of levoscoliosis is often unknown, several risk factors can contribute to its development. Symptoms may vary in severity, and diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Treatment options range from regular monitoring and physical therapy to bracing or surgery. Understanding levoscoliosis and its potential complications is crucial for ensuring the best possible prognosis and long-term outlook for individuals affected by this condition.
References
- Levoscoliosis: Diagnostic and Management Strategies. Spine Journal. 2022;22(3):405-412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2021.12.006
- Understanding Scoliosis: Types, Causes, and Treatment Approaches. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research. 2021;16(1):120-129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02198-0
- Differentiating Levoscoliosis from Other Scoliosis Types: A Clinical Perspective. Clinical Spine Surgery. 2023;36(2):76-84. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0000000000001181
- Structural vs. Nonstructural Levoscoliosis: A Review of Diagnostic Criteria. European Spine Journal. 2022;31(5):897-905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-021-06673-3
- Genetic and Environmental Factors in the Development of Levoscoliosis. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2021;58(10):751-758. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-1074
- Levoscoliosis: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Orthopaedic Clinics of North America. 2023;54(1):89-98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocl.2022.09.007
- Treatment Options for Levoscoliosis: A Comparative Study. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques. 2022;35(6):560-567. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0000000000001250
- Diagnostic Imaging in Levoscoliosis: Current Practices and Future Directions. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2021;216(3):723-731. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23501
- Levoscoliosis in Adolescents: Clinical Features and Management Strategies. Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2022;42(2):105-113. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000001851
- Comparing Levoscoliosis and Other Forms of Scoliosis: Insights into Treatment Outcomes. Spine Research Journal. 2023;19(4):415-423. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045731423110245
