Scoliosis is a condition that results in an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. It can develop at any age but is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence. The curvature may appear as an “S” or “C” shape, and its severity ranges from mild to severe. Factors contributing to scoliosis include genetic predisposition, neuromuscular conditions, and sometimes unknown causes. The severity can necessitate extensive medical intervention and ongoing treatment.
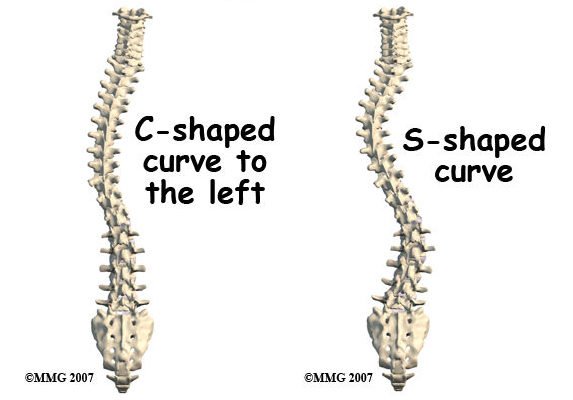
Types and Severity of Scoliosis
Scoliosis is classified into several types:
- Idiopathic Scoliosis: The most common type, with no known cause.
- Congenital Scoliosis: Present at birth due to spinal abnormalities.
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis: Resulting from conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
Severity is measured by the degree of spinal curvature:
- Mild Scoliosis: Curvature between 10 and 25 degrees.
- Moderate Scoliosis: Curvature between 25 and 40 degrees.
- Severe Scoliosis: Curvature greater than 40 degrees.
Disability Benefits and Eligibility
To qualify for disability benefits, individuals must meet the Social Security Administration’s (SSA) definition of disability, which includes having a severe medical condition that prevents substantial gainful activity (SGA) and is expected to last for at least 12 months or result in death. Scoliosis may meet these criteria if it significantly impairs the ability to perform work-related activities.
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
SSDI provides benefits to individuals who have contributed to the Social Security system through their work history. Eligibility requires sufficient work credits and a recent work history. The impact of scoliosis on an individual’s ability to work will be evaluated to determine SSDI eligibility.

Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
SSI is a needs-based program offering benefits to individuals with limited income and resources. Unlike SSDI, SSI does not require work credits. Eligibility is determined based on financial need and the severity of the medical condition. Individuals with scoliosis who meet the income and resource limits may qualify for SSI benefits.

Medical Evidence and Documentation
Comprehensive medical evidence is crucial when applying for disability benefits. This includes medical records, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRIs), and documentation from healthcare professionals. The evidence should clearly demonstrate the scoliosis diagnosis, its severity, and its impact on the individual’s functionality.
Meeting the Listing Requirements
The SSA’s Blue Book lists specific criteria for various medical conditions to qualify for disability benefits. Although scoliosis is not specifically listed, it can qualify under other listings, such as musculoskeletal disorders or spinal disorders. The severity of scoliosis and any related complications will be evaluated to determine if the criteria are met.
Residual Functional Capacity (RFC) Assessment
If scoliosis does not meet the specific criteria in the Blue Book, the SSA will assess residual functional capacity (RFC). This assessment evaluates an individual’s ability to perform work-related activities considering physical and mental limitations caused by scoliosis. Factors assessed include the ability to sit, stand, walk, lift, and perform tasks required for various jobs.
Applying for Disability Benefits
Applications for disability benefits can be submitted online, by phone, or in person at a local Social Security office. The application requires detailed information about the individual’s medical condition, work history, and financial situation. Accurate and thorough information is essential for a fair evaluation.
Appeals and Denials
Disability claims are often initially denied. If a claim is denied, individuals have the right to appeal. The appeals process includes reconsideration, a hearing before an administrative law judge, and further appeals to the Appeals Council and federal court if necessary. Legal representation or assistance from a disability advocate can improve the chances of a successful appeal.
Conclusão
Not all individuals with scoliosis will qualify for disability benefits, but those with severe cases that impact their ability to work may be eligible for SSDI or SSI programs. Success in a disability claim depends on providing comprehensive medical evidence, meeting listing requirements, or demonstrating a significant impact on residual functional capacity. Understanding the criteria and application process can help individuals with scoliosis navigate the disability benefits system and secure financial support.
Referências
- [1] Instituto Nacional de Artrite e Doenças Musculoesqueléticas e da Pele. 'Scoliosis' (Escoliose). Disponível em: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/scoliosis
- [2] American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine. ‘Scoliosis: Overview and Treatment.’ Available at: https://www.aanem.org/Patients/Disorders/Scoliosis
- [3] National Scoliosis Foundation. ‘Understanding Scoliosis.’ Available at: https://www.scoliosis.org/about-scoliosis/
- [4] Social Security Administration. ‘Disability Benefits.’ Available at: https://www.ssa.gov/benefits/disability/
- [5] Social Security Administration. ‘Supplemental Security Income (SSI).’ Available at: https://www.ssa.gov/ssi/
- [6] Mayo Clinic. ‘Scoliosis: Symptoms and Causes.’ Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/scoliosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351526
- [7] National Organization for Rare Disorders. ‘Scoliosis.’ Available at: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/scoliosis/
- [8] National Health Service. ‘Scoliosis.’ Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/scoliosis/
- [9] U.S. Social Security Administration. ‘Blue Book: Disability Evaluation Under Social Security.’ Available at: https://www.ssa.gov/disability/professionals/bluebook/
- [10] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ‘Scoliosis Overview.’ Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/scoliosis/index.html
- [11] MedlinePlus. ‘Scoliosis.’ Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/scoliosis.html
- [12] Cleveland Clinic. ‘Scoliosis Diagnosis and Treatment.’ Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16860-scoliosis
- [13] WebMD. ‘Scoliosis.’ Available at: https://www.webmd.com/back-pain/guide/scoliosis
- [14] Healthline. ‘Scoliosis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment.’ Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/scoliosis
- [15] Orthopaedic Foundation. ‘Scoliosis and Disability Benefits.’ Available at: https://www.orthopaedicfoundation.org/scoliosis-disability-benefits/

