Scoliosis Metal Rod: Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. In severe cases, where the curvature progresses rapidly or causes significant pain and discomfort, surgery may be recommended. One common surgical intervention for scoliosis is the insertion of metal rods into the spine. These rods serve to correct and stabilize the curvature, allowing for improved spinal alignment and function. Understanding the purpose, types, surgical procedure, benefits, risks, long-term effects, and alternative treatments of metal rods in scoliosis surgery is crucial for patients and their families.
The Purpose of Metal Rods in Scoliosis Surgery
The primary purpose of metal rods in scoliosis surgery is to correct the abnormal curvature of the spine and prevent further progression. By attaching the rods to the vertebrae, surgeons can straighten the spine and hold it in the corrected position. This stabilization allows for improved spinal alignment, reduces pain, and enhances overall function. Metal rods provide the necessary support to maintain the corrected position while the spine heals and fuses.
Types of Metal Rods Used in Scoliosis Surgery
Several types of metal rods are used in scoliosis surgery, including stainless steel, titanium, and cobalt-chromium alloys. Stainless steel rods have been used for many years and are known for their strength and durability. Titanium rods, on the other hand, are lighter and more flexible, allowing for better contouring to the spine. Cobalt-chromium rods offer a balance between strength and flexibility. The choice of rod material depends on various factors, including the severity of the curvature, patient age, and surgeon preference.

The Surgical Procedure for Inserting Metal Rods
Scoliosis Metal Rod: The surgical procedure for inserting metal rods in scoliosis surgery is known as spinal fusion. During this procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the back and exposes the affected area of the spine. The abnormal vertebrae are then realigned using various techniques, such as osteotomy or vertebral derotation. Once the desired correction is achieved, the metal rods are attached to the vertebrae using screws, hooks, or wires. Bone grafts or bone substitutes are often used to promote fusion between the vertebrae, ensuring long-term stability.
Benefits and Risks of Metal Rods in Scoliosis Surgery
The use of metal rods in scoliosis surgery offers several benefits. Firstly, it allows for significant correction of the spinal curvature, leading to improved posture and appearance. Secondly, metal rods provide stability and support, reducing pain and discomfort. Additionally, metal rods can prevent further progression of the curvature, minimizing the need for future surgeries. However, like any surgical procedure, there are risks involved. These include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and complications associated with anesthesia. It is essential for patients to discuss these risks with their surgeon and make an informed decision.
Long-Term Effects of Metal Rods on Spinal Alignment
The long-term effects of metal rods on spinal alignment are generally positive. Studies have shown that metal rod insertion can lead to significant improvement in spinal curvature, with a high rate of successful correction. The rods provide stability and prevent the spine from reverting to its original curvature. However, it is important to note that the spine may continue to grow after surgery, potentially affecting the alignment. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are necessary to ensure that the rods continue to provide the desired correction.
Impact of Metal Rods on Range of Motion and Flexibility
Metal rods in scoliosis surgery can have an impact on the range of motion and flexibility of the spine. While the rods provide stability, they also limit the natural movement of the spine. This restriction can affect activities such as bending, twisting, and stretching. However, it is important to note that the degree of limitation varies depending on the type of rod used and the surgical technique employed. Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a crucial role in maintaining and improving range of motion and flexibility after metal rod insertion.
Potential Complications Associated with Metal Rods
Although metal rods are generally safe and effective, there are potential complications associated with their use. These include rod breakage, rod migration, and implant failure. Rod breakage can occur due to excessive stress on the rods or poor bone quality. Rod migration refers to the movement of the rods from their intended position, which can lead to loss of correction. Implant failure can occur if the screws or hooks used to attach the rods to the vertebrae become loose or dislodged. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential to detect and address these complications promptly.
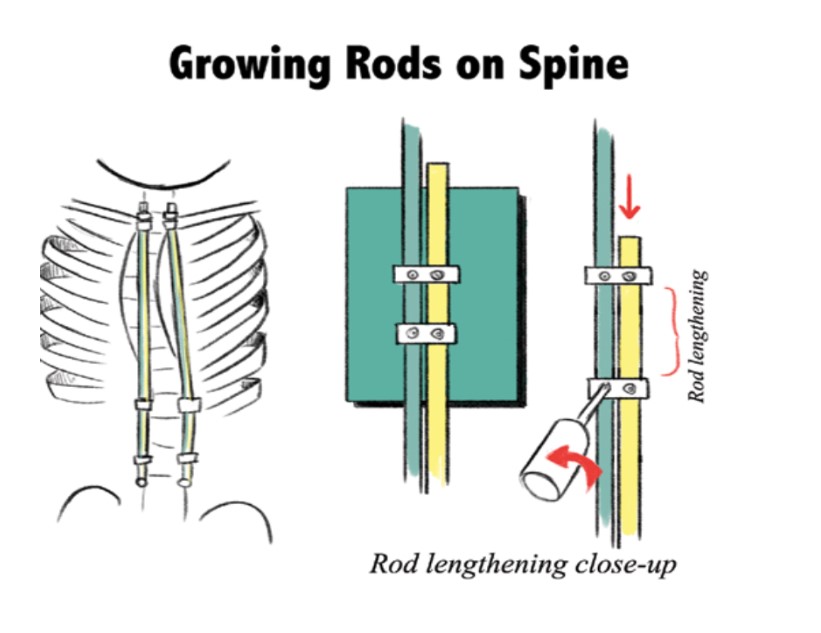
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy after Metal Rod Insertion
Rehabilitation and physical therapy play a crucial role in the recovery and long-term success of scoliosis surgery with metal rod insertion. Physical therapists work closely with patients to develop personalized exercise programs that focus on strengthening the core muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall function. These exercises help patients regain strength, improve posture, and adapt to the limitations imposed by the metal rods. Rehabilitation and physical therapy also provide emotional support and guidance throughout the recovery process.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Care for Patients with Metal Rods
Patients who undergo scoliosis surgery with metal rod insertion require regular monitoring and follow-up care. This includes periodic X-rays to assess the alignment of the spine and the condition of the metal rods. The frequency of follow-up visits may vary depending on the patient’s age, the severity of the curvature, and the surgeon’s recommendations. Monitoring and follow-up care are essential to detect any complications or changes in the spinal alignment and ensure the long-term success of the surgery.
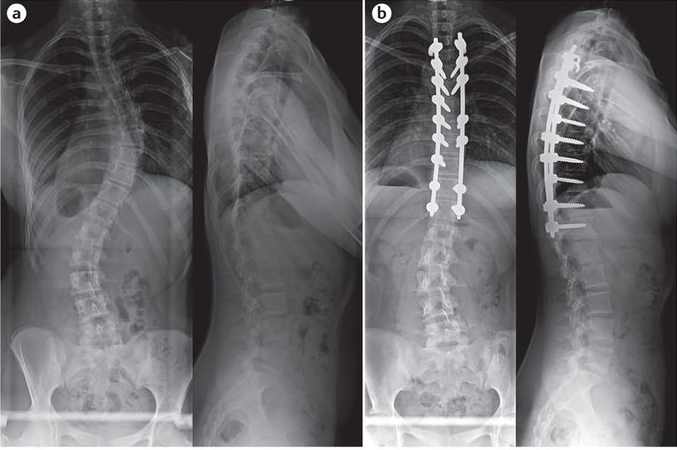
Alternative Treatments to Metal Rods in Scoliosis Surgery
While metal rods are a common and effective treatment for scoliosis, there are alternative treatments available. One such alternative is the use of non-fusion techniques, such as vertebral body tethering or growth modulation. These techniques aim to correct the curvature while preserving spinal motion. Another alternative is the use of bracing, which can help slow down the progression of the curvature in some cases. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of the curvature, patient age, and individual preferences.
Conclusion: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Metal Rods in Scoliosis Treatment
Metal rods have proven to be an effective treatment option for scoliosis, providing significant correction of the spinal curvature and improving overall function. While there are risks and potential complications associated with their use, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks. The long-term effects of metal rods on spinal alignment are generally positive, with a high rate of successful correction. However, it is important for patients to be aware of the impact on range of motion and flexibility and to engage in rehabilitation and physical therapy to optimize their recovery. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are crucial to ensure the continued success of the surgery. Alternative treatments may be considered in certain cases, depending on individual factors. Overall, metal rods in scoliosis surgery have revolutionized the treatment of this condition, providing patients with improved quality of life and long-term spinal stability.
References
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. “Scoliosis.” https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/scoliosis.
- Mayo Clinic. “Scoliosis Symptoms and Causes.” https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/scoliosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351782.
- Cleveland Clinic. “Scoliosis.” https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4394-scoliosis.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. “Scoliosis Treatment.” https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/scoliosis/treatment.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. “Scoliosis: Overview.” https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/scoliosis/.
- Scoliosis Research Society. “Scoliosis Basics.” https://www.srs.org/professionals/education-and-training/resources/scoliosis-basics.
- National Scoliosis Foundation. “Scoliosis and Breathing.” https://www.scoliosisfoundation.org/scoliosis-and-breathing.
- PubMed Central. “The Role of Breathing Exercises in Scoliosis Management.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4121910/.
- Journal of Physical Therapy Science. “Breathing Exercises and Scoliosis: A Review.” https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jpts/30/2/30_228/_article.
- European Spine Journal. “Effect of Breathing Exercises on Respiratory Function in Scoliosis Patients.” https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00586-018-5789-3.

