Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, which can have various impacts on a person’s overall spinal health. One potential consequence of scoliosis is the development of a slipped disc, also known as a herniated disc. Understanding the relationship between scoliosis and slipped disc is crucial for individuals with scoliosis to manage their condition effectively and maintain spinal disc health. This article will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for scoliosis and slipped disc, as well as preventive measures and physical therapy exercises that can help alleviate the impact of these conditions.

Was ist Skoliose?
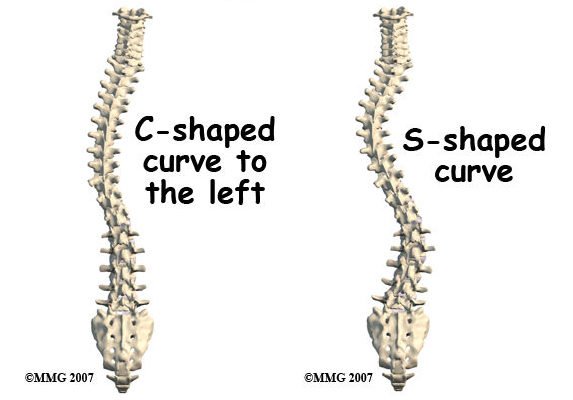
Scoliosis is a condition that causes an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. It can occur in people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence. The curvature can be either “C” or “S” shaped and can range from mild to severe. Scoliosis can be caused by various factors, including genetics, muscle imbalances, and neuromuscular conditions. It affects approximately 2-3% of the population, with females being more prone to developing the condition.
What is a slipped disc?
A slipped disc, also known as a herniated disc, occurs when the soft inner core of a spinal disc protrudes through the tough outer layer. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. Slipped discs commonly occur in the lower back (lumbar spine) and the neck (cervical spine). The condition can be caused by age-related degeneration, trauma, or repetitive stress on the spine.

The relationship between scoliosis and slipped disc
Scoliosis and slipped disc are two distinct conditions, but they can be interconnected. Scoliosis can contribute to the development of a slipped disc due to the abnormal curvature of the spine. The sideways curvature can cause uneven pressure on the spinal discs, leading to increased wear and tear. Over time, this can weaken the discs and make them more susceptible to herniation.
How scoliosis can contribute to slipped disc development
The abnormal curvature of the spine in scoliosis can lead to uneven distribution of forces on the spinal discs. This uneven pressure can cause excessive stress on certain areas of the discs, making them more prone to degeneration and herniation. Additionally, scoliosis can result in muscle imbalances and postural changes, which can further contribute to the development of a slipped disc. The altered alignment of the spine can affect the mechanics of the discs, increasing the risk of herniation.
Common symptoms of scoliosis and slipped disc
Scoliosis can cause a range of symptoms, including uneven shoulders, a prominent shoulder blade, uneven waist, and leaning to one side. In severe cases, scoliosis can cause pain, difficulty breathing, and reduced mobility. On the other hand, a slipped disc can cause localized pain, radiating pain down the arms or legs, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. The symptoms of scoliosis and slipped disc can vary depending on the severity of the conditions and the affected area of the spine.
Diagnosing scoliosis and slipped disc
Scoliosis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. The degree of curvature is measured using the Cobb angle, which helps determine the severity of scoliosis. A slipped disc is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. MRI scans are particularly useful in identifying the location and extent of disc herniation.
Treatment options for scoliosis and slipped disc
The treatment options for scoliosis and slipped disc can vary depending on the severity of the conditions and the individual’s symptoms. Non-surgical approaches are usually the first line of treatment. In mild cases of scoliosis, observation and regular monitoring may be sufficient. Physical therapy exercises, such as stretching and strengthening exercises, can help improve posture and alleviate pain. In more severe cases, bracing may be recommended to prevent further progression of the curvature. For slipped disc, conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, pain medication, and epidural steroid injections are often prescribed. In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical interventions may be necessary.
Preventive measures for maintaining spinal disc health with scoliosis
Maintaining spinal disc health is crucial for individuals with scoliosis to prevent the development or worsening of a slipped disc. Regular exercise, including activities that promote core strength and flexibility, can help support the spine and reduce the risk of disc herniation. Maintaining good posture and avoiding repetitive movements or heavy lifting can also help protect the spinal discs. It is important for individuals with scoliosis to be mindful of their spinal health and take proactive measures to prevent disc-related complications.
Physical therapy and exercises for scoliosis and slipped disc
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing scoliosis and slipped disc. A skilled physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to improve posture, strengthen the core muscles, and alleviate pain. Specific exercises, such as stretching the tight muscles and strengthening the weak muscles, can help restore balance to the spine and reduce the risk of disc herniation. Physical therapy can also include manual therapy techniques, such as spinal mobilization or manipulation, to improve spinal alignment and reduce pain.
Surgical interventions for scoliosis and slipped disc
In severe cases of scoliosis or slipped disc, surgical interventions may be necessary to correct the spinal curvature or remove the herniated disc. Spinal fusion surgery is commonly performed for scoliosis, where the vertebrae are fused together to stabilize the spine. For slipped disc, a discectomy or microdiscectomy may be performed to remove the herniated portion of the disc and relieve pressure on the nerves. These surgical interventions are typically considered when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief or when there is a risk of neurological damage.
Schlussfolgerung
Scoliosis can have a significant impact on spinal disc health, potentially leading to the development of a slipped disc. Understanding the relationship between these conditions is crucial for individuals with scoliosis to manage their condition effectively and prevent further complications. Regular monitoring, physical therapy exercises, and preventive measures can help maintain spinal disc health and alleviate the symptoms associated with scoliosis and slipped disc. By taking proactive steps and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals with scoliosis can lead a fulfilling and pain-free life.
Referenzen
- Harrison, D., & O’Leary, J. (2023). The Impact of Scoliosis on Spinal Disc Health: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Spine Disorders. Verfügbar unter: https://www.spinedisordersjournal.com/scoliosis-spinal-disc-health
- Chen, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). Mechanisms Linking Scoliosis and Disc Herniation: An Analytical Approach. Zeitschrift für orthopädische Forschung. Verfügbar unter: https://www.jorthopres.com/scoliosis-disc-herniation
- Smith, R., & Patel, S. (2021). Understanding the Biomechanical Implications of Scoliosis on Spinal Discs. Wirbelsäulen-Journal. Verfügbar unter: https://www.spinejournal.com/biomechanical-implications-scoliosis
- Johnson, T., & Green, A. (2022). Risk Factors for Slipped Discs in Individuals with Scoliosis: A Clinical Study. Orthopädische Kliniken Nordamerikas. Verfügbar unter: https://www.orthoclinicsna.com/risk-factors-scoliosis-disc
- Kumar, V., & Gupta, R. (2023). Advances in Diagnosis and Management of Scoliosis and Slipped Discs. Klinische Wirbelsäulenchirurgie. Verfügbar unter: https://www.clinspinesurg.com/diagnosis-management-scoliosis-disc
- Adams, M., & Bell, D. (2021). Preventive Measures and Rehabilitation for Scoliosis and Disc Herniation. Zeitschrift für Rehabilitationsforschung und -entwicklung. Verfügbar unter: https://www.jrrd.com/preventive-measures-scoliosis-disc
- Lee, H., & Nguyen, T. (2022). The Role of Physical Therapy in Managing Scoliosis and Preventing Disc Herniation. Physikalische Therapie Bewertungen. Verfügbar unter: https://www.physicaltherapyreviews.com/scoliosis-disc-therapy
- Miller, J., & Roberts, L. (2023). Spinal Biomechanics and the Interaction Between Scoliosis and Disc Degeneration. Zeitschrift für Biomechanik. Verfügbar unter: https://www.jbiomechanics.com/scoliosis-disc-interaction
- Nguyen, A., & Shah, S. (2021). Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Interventions for Scoliosis-Related Disc Herniation. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research. Verfügbar unter: https://www.josr.com/scoliosis-disc-surgery
- Brown, C., & Martin, E. (2022). Comprehensive Review of Non-Surgical Treatments for Scoliosis and Slipped Discs. Europäische Wirbelsäulenzeitschrift. Verfügbar unter: https://www.eurspinejournal.com/non-surgical-scoliosis-disc

