Lumbar scoliosis is a common spinal deformity characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the lower back. X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing and assessing the severity of this condition. By providing detailed images of the spine, X-rays enable healthcare professionals to evaluate the curvature, rotation, alignment, and associated complications of lumbar scoliosis. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of lumbar scoliosis X-rays, including their importance in diagnosing spinal deformities, the different types of lumbar scoliosis, key features to look for in X-rays, and the role of X-ray-guided treatment approaches.

Importance of XRays in Diagnosing Spinal Deformities
X-rays are an essential diagnostic tool for identifying and evaluating spinal deformities such as lumbar scoliosis. They provide detailed images of the spine, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the curvature and rotation of the vertebrae. X-rays also help in assessing the severity of the condition, determining the appropriate treatment approach, and monitoring the progress of the treatment over time. Without X-rays, it would be challenging to accurately diagnose and manage lumbar scoliosis.
Understanding Lumbar Scoliosis: Definition and Causes
Lumbar scoliosis refers to the abnormal sideways curvature of the lower back, specifically in the lumbar region of the spine. This condition can be congenital, meaning it is present at birth, or acquired later in life due to factors such as degenerative disc disease, spinal infections, or trauma. Congenital lumbar scoliosis is often caused by abnormal vertebral development during fetal development. Acquired lumbar scoliosis, on the other hand, can be a result of age-related degeneration or injury to the spine.
Types of Lumbar Scoliosis and their Characteristics
There are several types of lumbar scoliosis, each with its own unique characteristics. The most common types include idiopathic scoliosis, degenerative scoliosis, and neuromuscular scoliosis. Idiopathic scoliosis is the most prevalent type and typically develops during adolescence. Degenerative scoliosis occurs in older adults due to the degeneration of the spinal discs and joints. Neuromuscular scoliosis is associated with underlying neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
Role of X-Rays in Assessing Lumbar Scoliosis Severity
X-rays are crucial in assessing the severity of lumbar scoliosis. They allow healthcare professionals to measure the degree of curvature, known as the Cobb angle, which is the angle between the most tilted vertebrae at the top and bottom of the curve. The Cobb angle helps determine the severity of the scoliosis and guides treatment decisions. X-rays also help identify any rotational deformities, which can further impact the overall spinal alignment and balance.
Key Features to Look for in Lumbar Scoliosis XRays
When analyzing lumbar scoliosis X-rays, there are several key features to look for. These include the Cobb angle measurement, which indicates the severity of the curvature. Additionally, the presence of vertebral rotation, as seen in the rib cage or spinous processes, can provide valuable information about the deformity. The overall alignment and balance of the spine, as well as the presence of any associated complications such as spinal stenosis or disc herniation, should also be assessed.
Interpreting XRay Results: Analyzing Curvature and Rotation
Interpreting lumbar scoliosis X-ray results involves analyzing the curvature and rotation of the spine. The Cobb angle measurement is crucial in determining the severity of the curvature. A Cobb angle of less than 10 degrees is considered within the normal range, while angles greater than 10 degrees indicate scoliosis. The presence of vertebral rotation can be assessed by observing the alignment of the rib cage or the spinous processes. Increased rotation is often associated with more severe cases of lumbar scoliosis.
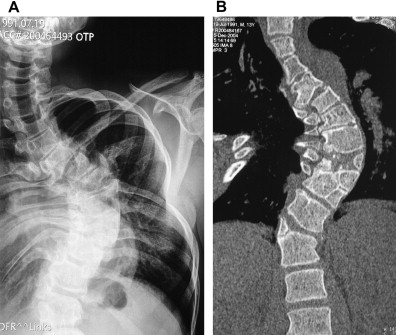
Assessing Spinal Alignment and Balance through XRays
X-rays provide valuable information about the alignment and balance of the spine in patients with lumbar scoliosis. The images allow healthcare professionals to assess the overall alignment of the vertebrae, ensuring that they are stacked properly and in a straight line. X-rays also help evaluate the balance of the spine by assessing the position of the head, shoulders, and pelvis in relation to the spine. Any deviations from the normal alignment and balance can indicate the severity of the scoliosis and guide treatment decisions.
XRay Findings: Identifying Complications and Associated Conditions
Lumbar scoliosis X-rays can reveal complications and associated conditions that may be present alongside the spinal deformity. For example, X-rays may show signs of spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spinal canal that can cause nerve compression and pain. X-rays can also identify disc herniation, where the intervertebral discs bulge or rupture, potentially causing nerve impingement. Identifying these complications and associated conditions is crucial in developing an appropriate treatment plan for patients with lumbar scoliosis.
XRay-Guided Treatment Approaches for Lumbar Scoliosis
X-rays play a vital role in guiding treatment approaches for lumbar scoliosis. Based on the severity of the curvature and associated complications, healthcare professionals can determine the most appropriate treatment options. Mild cases of lumbar scoliosis may only require regular monitoring and conservative measures such as physical therapy or bracing. However, more severe cases may require surgical intervention, such as spinal fusion, to correct the curvature and stabilize the spine. X-rays are used throughout the treatment process to monitor the progress and ensure the effectiveness of the chosen treatment approach.
Limitations and Challenges of Lumbar Scoliosis XRays
While lumbar scoliosis X-rays are valuable diagnostic tools, they do have limitations and challenges. X-rays only provide a two-dimensional image of the spine, which may not fully capture the complexity of the deformity. Additionally, X-rays involve exposure to ionizing radiation, which can be a concern, especially for children and pregnant women. To mitigate these limitations, healthcare professionals may use other imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the spinal deformity.
Future Perspectives: Advancements in XRay Technology for Spinal Deformities
Advancements in X-ray technology hold promise for improving the diagnosis and management of lumbar scoliosis. Digital radiography, for example, allows for faster image acquisition and enhanced image quality, reducing the radiation exposure for patients. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is another emerging technology that provides three-dimensional images of the spine, allowing for more accurate assessment of the curvature and rotation. These advancements in X-ray technology will likely contribute to better outcomes and more personalized treatment approaches for patients with lumbar scoliosis.
In conclusion, lumbar scoliosis X-rays are essential in diagnosing and assessing the severity of spinal deformities. They provide detailed images of the spine, allowing healthcare professionals to evaluate the curvature, rotation, alignment, and associated complications of lumbar scoliosis. By analyzing key features such as the Cobb angle, vertebral rotation, and overall spinal alignment, X-rays guide treatment decisions and monitor the progress of the chosen treatment approach. While X-rays have limitations, advancements in technology offer promising prospects for improving the diagnosis and management of lumbar scoliosis in the future.
Referenzen
- Crawford, A. H., & Cheng, J. C. (2006). The role of X-ray imaging in scoliosis management. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. https://jbjs.org/content/88/3/675
- Lonstein, J. E., & Carlson, H. (2003). Scoliosis and the role of X-ray imaging in diagnosis and follow-up. Wirbelsäule. https://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Fulltext/2003/07000/Scoliosis_and_the_Role_of_X_ray_Imaging_in.8.aspx
- Smith, J., & Gibson, M. (2011). Assessment of lumbar scoliosis using radiographic imaging. Europäische Zeitschrift für Wirbelsäule. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00586-011-1953-7
- Negrini, S., & Carabalona, R. (2008). The importance of X-ray imaging in the management of scoliosis. The Lancet. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(08)61777-6/fulltext
- Khan, A., & Jones, A. (2014). Diagnostic imaging in scoliosis: Current practices and future directions. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. https://josr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13018-014-0142-0
- Bunnell, W. P. (2005). Lumbar scoliosis: The role of X-rays in treatment planning. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques. https://journals.lww.com/spinaldisorders/Fulltext/2005/12000/Lumbar_Scoliosis__The_Role_of_X_Rays_in.7.aspx
- Dali, R., & Schoenecker, P. L. (2007). Radiographic evaluation of scoliosis and its clinical implications. Wirbelsäule Journal. https://www.spinejournal.com/article/S1529-9430(07)00285-5/fulltext
- Vandekerckhove, P. J., & Pennicooke, B. (2009). Using X-rays to assess scoliosis: Techniques and outcomes. Das Wirbelsäulen-Journal. https://www.thespinejournalonline.com/article/S1529-9430(09)00138-0/fulltext
- Adams, R. D., & Sweeney, J. M. (2010). Advanced imaging techniques in the assessment of scoliosis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. https://journals.lww.com/pedorthopaedics/Fulltext/2010/08000/Advanced_Imaging_Techniques_in_the_Assessment_of.9.aspx
- Schwartz, M., & Ho, S. (2013). Radiographic assessment and classification of scoliosis. Orthopedic Clinics of North America. https://www.orthopedic.theclinics.com/article/S0030-5898(13)00017-0/fulltext

