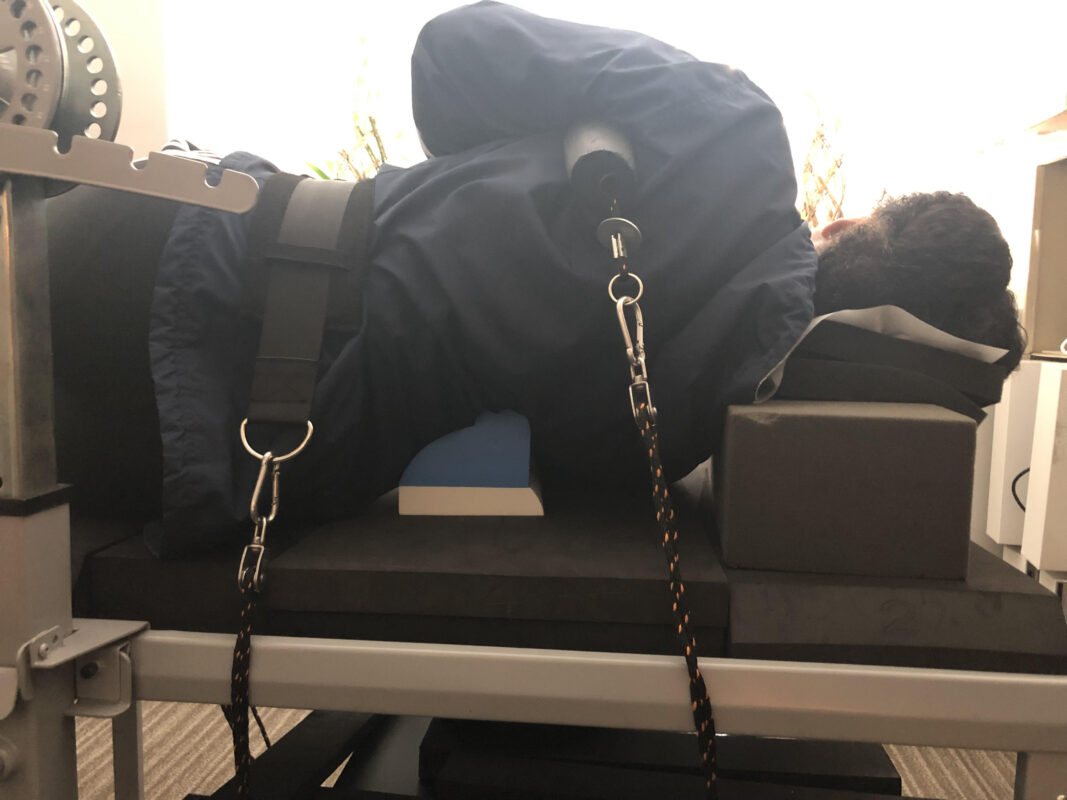
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. It affects approximately 2-3% of the population, with the majority of cases occurring in adolescents. The condition can cause pain, discomfort, and even deformity if left untreated. Scoliosis traction is a non-surgical treatment option that aims to correct the curvature of the spine and provide spinal support. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of scoliosis traction, including its techniques, equipment, mechanics, benefits, risks, and its role in combination with other treatment modalities.

What is scoliosis and how does it affect the spine?
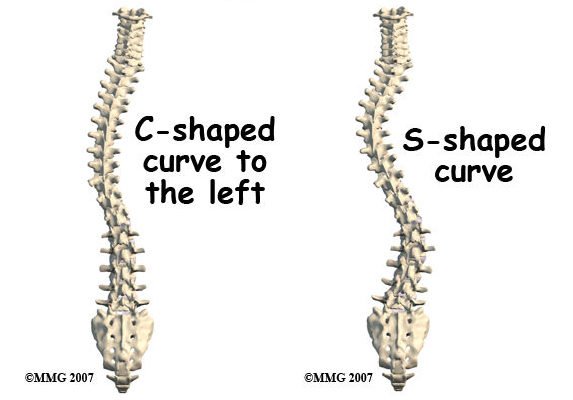
Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine curves sideways, forming an “S” or “C” shape. It can occur in any part of the spine, but the most common types are thoracic (affecting the upper back) and lumbar (affecting the lower back). The exact cause of scoliosis is often unknown, but it can be influenced by factors such as genetics, muscle imbalances, and neuromuscular conditions.
The abnormal curvature of the spine in scoliosis can lead to a range of symptoms and complications. These may include back pain, muscle stiffness, reduced range of motion, breathing difficulties, and even psychological distress due to changes in body image. If left untreated, scoliosis can progress and result in a noticeable deformity, affecting the individual’s overall quality of life.
The role of traction in scoliosis treatment
Scoliosis traction is a therapeutic technique used to apply controlled forces to the spine in order to correct the curvature and provide spinal support. It is often used as a non-surgical treatment option for mild to moderate cases of scoliosis, particularly in adolescents who are still growing. Traction works by gradually stretching the spine, allowing for the realignment of the vertebrae and the correction of the abnormal curvature.
Different techniques of scoliosis traction
There are several techniques of scoliosis traction that can be used depending on the severity and location of the curvature. The most common techniques include manual traction, mechanical traction, and positional traction.
Manual traction involves the application of controlled forces by a trained therapist using their hands. This technique allows for precise adjustments and can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Mechanical traction, on the other hand, utilizes specialized devices to apply the necessary forces to the spine. These devices can be adjusted to provide a consistent and controlled pull on the spine. Positional traction involves placing the individual in specific positions to encourage the correction of the curvature.
Traction devices and equipment used in scoliosis treatment
Various devices and equipment are used in scoliosis traction therapy to facilitate the application of controlled forces to the spine. These may include traction tables, harnesses, pulleys, weights, and straps. Traction tables provide a stable surface for the individual to lie on while the traction forces are applied. Harnesses and straps are used to secure the individual to the table and ensure proper alignment during the procedure. Pulleys and weights are used to create the necessary tension and pull on the spine.
Understanding the mechanics of scoliosis traction
The mechanics of scoliosis traction involve the application of controlled forces to the spine in order to stretch and realign the vertebrae. By applying a consistent and gradual pull, traction therapy aims to correct the abnormal curvature and restore the spine’s natural alignment. The forces applied during traction therapy can help to elongate the spine, decompress the discs, and improve the flexibility of the muscles and ligaments surrounding the spine.
Benefits and potential risks of scoliosis traction
Scoliosis traction offers several benefits as a non-surgical treatment option for scoliosis. It can help to reduce the curvature of the spine, alleviate pain and discomfort, improve posture, and enhance overall spinal function. Traction therapy can also prevent the progression of scoliosis and the development of further complications. Additionally, scoliosis traction is a non-invasive and relatively safe treatment option, especially when performed by trained professionals.
However, like any medical procedure, scoliosis traction does carry some potential risks. These may include muscle soreness, temporary discomfort during the procedure, and the possibility of aggravating existing spinal conditions. It is important for individuals considering traction therapy to consult with their healthcare provider and undergo a thorough evaluation to determine if they are suitable candidates for this treatment modality.
Preparing for scoliosis traction therapy
Before undergoing scoliosis traction therapy, individuals will typically undergo a comprehensive evaluation to assess the severity and location of the curvature, as well as their overall health and suitability for the procedure. This evaluation may involve physical examinations, X-rays, and other diagnostic tests. Based on the evaluation, a customized treatment plan will be developed, which may include a combination of traction therapy and other treatment modalities.
Step-by-step guide to scoliosis traction procedure
The scoliosis traction procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The individual is positioned on a traction table and secured with harnesses and straps to ensure proper alignment.
- Application of traction forces: The traction device or equipment is adjusted to apply the necessary forces to the spine. This may involve the use of pulleys, weights, or mechanical devices.
- Gradual stretching: The forces are gradually increased over time to stretch the spine and correct the curvature. This process is typically performed under the supervision of a trained therapist.
- Monitoring and adjustments: The therapist closely monitors the individual’s response to the traction forces and makes any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal results.
- Duration and frequency: The duration and frequency of traction therapy sessions may vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and treatment plan. Sessions may last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours and may be performed multiple times per week.
Monitoring progress and adjusting traction therapy
Throughout the course of scoliosis traction therapy, the individual’s progress is closely monitored to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and make any necessary adjustments. This may involve regular physical examinations, X-rays, and other diagnostic tests to evaluate changes in the curvature and overall spinal alignment. Based on the monitoring results, the therapist may modify the traction forces, duration, or frequency of the therapy to optimize the outcomes.

Combining scoliosis traction with other treatment modalities
Scoliosis traction is often used in combination with other treatment modalities to achieve the best possible outcomes. These may include exercises, physical therapy, bracing, and chiropractic care. By combining different treatment approaches, healthcare providers can address the various aspects of scoliosis, including the correction of the curvature, improvement of muscle imbalances, and enhancement of overall spinal function.
Future developments and advancements in scoliosis traction therapy
As technology and medical knowledge continue to advance, there are ongoing developments and advancements in scoliosis traction therapy. These may include the use of computer-assisted traction devices, virtual reality-based rehabilitation programs, and personalized treatment plans based on individualized biomechanical assessments. These advancements aim to further improve the effectiveness, efficiency, and patient experience of scoliosis traction therapy.
In conclusion, scoliosis traction is a valuable non-surgical treatment option for individuals with scoliosis. It involves the application of controlled forces to the spine to correct the curvature and provide spinal support. With various techniques, devices, and equipment, scoliosis traction therapy can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs. While it offers several benefits, it is important to consider the potential risks and consult with healthcare professionals before undergoing traction therapy. By combining traction with other treatment modalities and monitoring progress, healthcare providers can optimize the outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals with scoliosis. With ongoing advancements in technology and research, the future of scoliosis traction therapy holds promise for further improvements in treatment effectiveness and patient care.
Références
- Hollingsworth, J. A., & Watanabe, J. (2017). Scoliosis traction: An overview of techniques and clinical outcomes. Journal des troubles et techniques de la colonne vertébrale. https://journals.lww.com/spinaldisorders/Abstract/2017/08000/Scoliosis_Traction__An_Overview_of_Techniques_and.2.aspx
- Zhu, F., & Zhang, X. (2016). Efficacy of traction therapy in scoliosis treatment: A systematic review. Journal de la colonne vertébrale. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1016/j.spinee.2016.03.019
- Schroth, H., & Weiss, H. R. (2011). Schroth method for scoliosis treatment: Principles and outcomes. European Spine Journal. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00586-011-1730-6
- Liu, X., & Zhang, T. (2018). Comparative study of manual vs mechanical traction for scoliosis. Clinical Rehabilitation. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0269215518788975
- Yang, J., & Xu, L. (2015). The role of scoliosis traction in combination with other treatments. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2325967115608320
- Khoshhal, K. I., & Alshammari, S. (2019). Scoliosis traction and its impact on spinal alignment: A review. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jor.24136
- Hsieh, P. H., & Tsai, M. H. (2020). Long-term outcomes of scoliosis traction therapy. Dos. https://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Fulltext/2020/01000/Long_term_Outcomes_of_Scoliosis_Traction_Therapy.6.aspx
- Mehta, J. S., & Newton, P. O. (2007). Scoliosis traction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Efficacy and clinical application. The Spine Journal. https://www.thespinejournalonline.com/article/S1529-9430(07)00768-5/fulltext
- Bach, J. R., & Farkas, G. (2014). Innovations in scoliosis traction and their clinical impact. Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S097656621400086X
- Sexton, M., & Riley, J. (2021). Assessing the effectiveness of scoliosis traction therapy: A meta-analysis. Journal de la chirurgie orthopédique et de la recherche. https://josr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13018-021-02323-4

