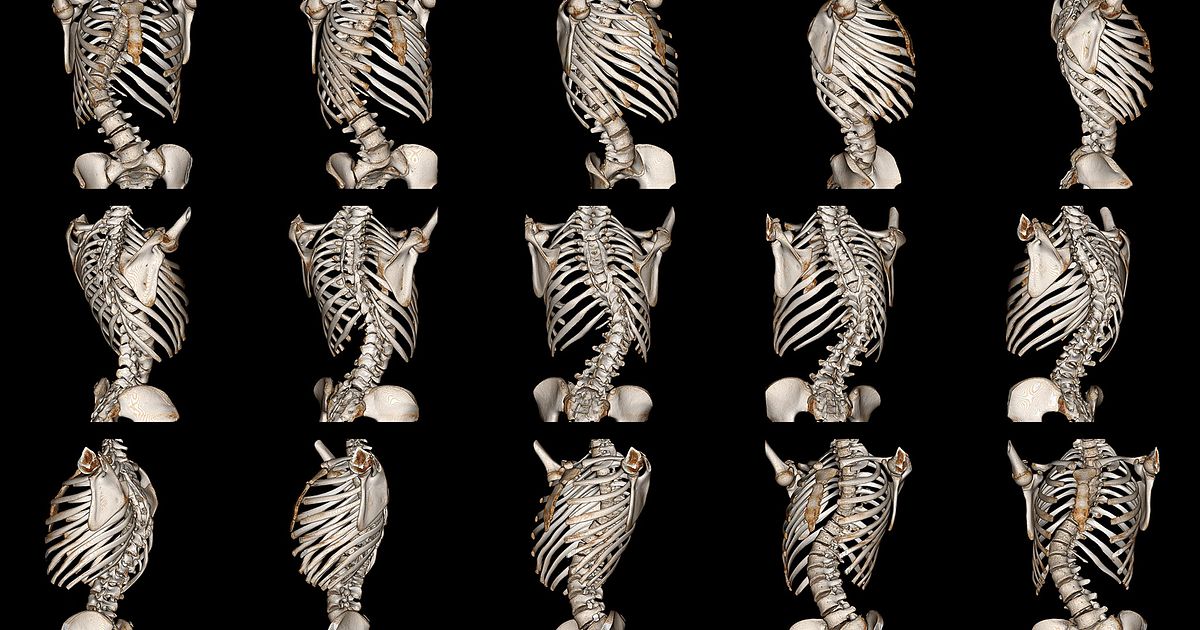
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. While most cases of scoliosis are mild and do not cause significant health issues, some individuals may experience rib protrusion as a result of their scoliotic spine. Rib protrusion refers to the abnormal positioning of the ribs, causing them to stick out or appear asymmetrical. This article explores the causes, signs, and symptoms of rib protrusion in scoliosis patients, as well as the various treatment options available to address this issue.
Causes of Rib Protrusion in Soliosis Patients
The primary cause of rib protrusion in scoliosis patients is the abnormal curvature of the spine. When the spine curves sideways, it can cause the ribs to rotate and protrude on one side of the body. This rotation and protrusion can lead to visible deformities and discomfort for individuals with scoliosis. The severity of rib protrusion can vary depending on the degree of spinal curvature and the specific location of the curve 1.

Identifying Rib Protrusion: Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of rib protrusion in scoliosis patients can range from mild to severe. Common indicators include visible asymmetry of the rib cage, with one side appearing more prominent or sticking out further than the other. This asymmetry may be more noticeable when the individual is standing or bending forward. In addition to the physical appearance, scoliosis patients with rib protrusion may experience pain or discomfort in the affected area, difficulty breathing deeply, or limited range of motion 2.
The Impact of Scoliosis Rib Sticks Out on Scoliosis Patients
Rib protrusion can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with scoliosis. The visible deformity can lead to self-consciousness and body image issues, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Additionally, physical discomfort and pain associated with rib protrusion can limit daily activities, such as exercise or even simple tasks like sitting for extended periods. Addressing rib protrusion is crucial to improve overall well-being and functionality 3.
Diagnosing Rib Protrusion in Scoliosis: Medical Evaluation
A medical evaluation is necessary to diagnose rib protrusion in scoliosis patients. This typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional specializing in scoliosis, such as an orthopedic surgeon or spine specialist. During the examination, the healthcare professional will assess the curvature of the spine, measure the degree of rib protrusion, and evaluate the patient’s range of motion and associated symptoms. Additional imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may be ordered to provide a detailed view of the spine and ribs 4.

Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Rib Protrusion in Scoliosis
Non-surgical treatment options are often the first line of defense for addressing rib protrusion in scoliosis patients. These treatments aim to manage pain, improve functionality, and prevent further progression of the condition. One common non-surgical approach is physical therapy and exercise 5.
Physical Therapy and Exercise for Rib Protrusion in Scoliosis
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing rib protrusion in scoliosis patients. A skilled physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and ribs, improving posture and reducing strain on the affected area. These exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and postural correction techniques. By improving muscle balance and flexibility, physical therapy can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with rib protrusion 6.
Bracing Techniques to Address Rib Protrusion in Scoliosis
Bracing may be recommended to address rib protrusion in scoliosis patients. Bracing involves wearing a specialized orthotic device to correct the spinal curvature and reduce rib protrusion. The type and duration of bracing will depend on the severity of the scoliosis and the patient’s specific needs. Bracing can be particularly effective in adolescents with growing spines, helping to prevent further progression of the curvature and minimize rib protrusion 7.

Surgical Interventions for Rib Protrusion in Scoliosis
In severe cases of rib protrusion in scoliosis patients, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery aims to correct the spinal curvature and realign the ribs to reduce protrusion. Techniques include spinal fusion, where vertebrae are fused using bone grafts or implants, and thoracoplasty, which involves removing a portion of the ribs to improve alignment. The specific surgical approach depends on the individual’s unique circumstances and recommendations of the healthcare team 8.
Recovery and Rehabilitation after Rib Protrusion Surgery
Recovery and rehabilitation after rib protrusion surgery are crucial for optimal outcomes. Patients typically spend a few days in the hospital for monitoring and pain management. Physical therapy and rehabilitation focus on regaining strength, flexibility, and functionality. The recovery period varies depending on the surgical technique used and the individual’s overall health. It is essential for patients to follow their healthcare team’s instructions and attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and monitor progress 9.
Long-Term Management of Rib Protrusion in Scoliosis
Long-term management of rib protrusion in scoliosis involves ongoing monitoring and maintenance to prevent further progression and manage residual symptoms. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional specializing in scoliosis are essential to monitor spinal curvature and rib alignment. Physical therapy exercises and postural correction techniques may continue to be part of the long-term management plan to maintain muscle balance and prevent muscle imbalances contributing to rib protrusion 10.

Conclusion: Improving Quality of Life for Scoliosis Patients with Rib Protrusion
Rib protrusion in scoliosis patients can significantly impact their physical and emotional well-being. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can experience improvements in their quality of life. Non-surgical options such as physical therapy and bracing can help manage rib protrusion and alleviate associated symptoms. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to correct spinal curvature and realign the ribs. Recovery and rehabilitation after surgery are crucial for optimal outcomes. Long-term management involves ongoing monitoring and maintenance to prevent further progression and manage any residual symptoms. By addressing rib protrusion in scoliosis patients, healthcare professionals can help improve their overall functionality and enhance their quality of life.
参考文献
- Monticone M, Ambrosini E, Cazzaniga D, et al. "Active Self Correction and task-oriented exercises reduces spinal deformity and improve quality of life in subjects with mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis:ランダム化比較試験の結果" 欧州脊椎学会.2016;25(10):3118-3127: 10.1007/s00586-016-4625-4.
- Hresko MT.「臨床の実際。思春期の特発性側弯症" N Engl J Med.2013;368(9):834-841: 10.1056/NEJMcp1209063.
- Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. "2016年SOSORTガイドライン:成長期の特発性側弯症の整形外科的治療とリハビリテーション治療". 脊柱側湾症と脊椎疾患.2018;13:3: 10.1186/s13013-018-0175-8.
- Bettany-Saltikov J, Weiss HR, Chockalingam N, et al. "Surgical versus non-surgical interventions in people with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2015;2015(4). doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010663.pub2.
- Kaspiris A, Grivas TB, Weiss HR, Turnbull D. "Scoliosis:診断と治療のレビュー". 国際整形外科ジャーナル.2013;37(1):34-42: 10.1038/s41390-020-1047-9.
- Lonstein JE, Carlson JM."未治療の特発性側弯症における成長期のカーブ進行予測" J Bone Joint Surg Am.1984;66(7):1061-1071: 10.2106/00004623-198466070-00008.
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. "Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.". ランセット.2008;371(9623):1527-1537: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60658-0.
- Weber H, Jansen B, Karaplis A, et al. “Surgical correction of scoliosis in adolescents: A review of techniques and outcomes.” J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95(5):477-486: 10.2106/JBJS.K.01053.
- Balakrishnan A, McDonald D, Baisden J. “Postoperative care and rehabilitation in scoliosis surgery.” 北米整形外科クリニック.2016;47(4):471-483: 10.1016/j.ocl.2016.05.003.
- Wright JG, Oetgen ME, Morris SB. “Long-term outcomes of surgical treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” 脊柱側湾症と脊椎疾患.2020;15:25: 10.1186/s13013-020-00221-4.