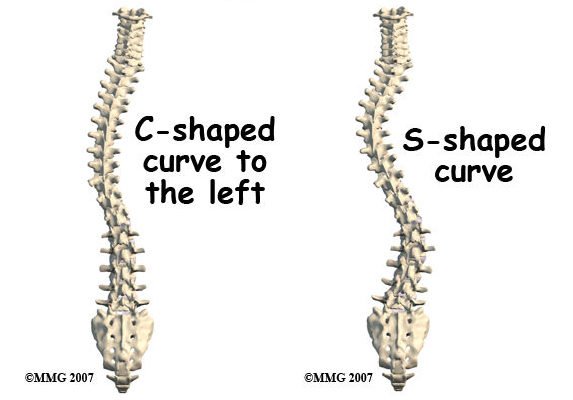
脊柱側湾症は、背骨の異常な湾曲を特徴とする疾患で、背骨が横に湾曲し、「S字」や「C字」の形になります。思春期特発性側弯症として知られるように、小児期や思春期に発症することもあれば、他の要因によって人生の後半になってから発症することもあります。脊柱側弯症の原因は必ずしも明らかではありませんが、遺伝的要因、神経筋疾患、背骨の構造異常などが関与している可能性があります。
障害の定義
障害とは一般的に、1つ以上の主要な生活活動を実質的に制限する身体的または精神的な障害と定義される。この定義は、個人の機能的制限と、日常業務を遂行する能力への影響を強調するものである。障害の法的定義は管轄区域によって異なり、法律や判例によって形成されることが多い。
障害をめぐる法的枠組み
米国を含む多くの国では、障害を持つアメリカ人法(ADA)やリハビリテーション法などの法律によって、障害に関する法的枠組みが確立されている。これらの法律は、障害者に対する差別を禁止し、雇用、公共サービス、公共の宿泊施設における合理的配慮を義務づけている。
脊柱側湾症は障害として認められるのか?
脊柱側弯症が障害として認められるかどうかは、その症状の重さと個人の日常生活への影響によって決まります。米国では、ADAは脊柱側弯症が歩行や持ち上げなどの1つ以上の主要な生活活動を実質的に制限する場合、障害とみなしています。しかし、その判断は、個人の具体的な状況や機能制限を考慮し、ケースバイケースで行われます。
脊柱側弯症に関する医学的見解
医学的見地から、脊柱側湾症は障害というよりも、むしろ医学的状態として主に捉えられています。医療専門家は、脊柱湾曲のさらなる進行を防ぎ、症状を管理するために、診断と治療に重点を置いています。治療には、重症度に応じて、経過観察、装具、手術などがあります。

脊柱側弯症の日常生活への影響
脊柱側湾症は、特に湾曲がひどい場合、日常生活に大きな影響を及ぼします。可動性、バランス、姿勢に影響を与え、特定の活動を困難にします。慢性的な痛み、疲労、身体活動への参加が困難になることもあります。自尊心の問題や社会的孤立など、感情的・心理的な影響も顕著です。
脊柱側湾症と雇用
脊柱側湾症が雇用に与える影響は、症状の重さや仕事の内容によって異なります。軽度の脊柱側弯症であれば職場のパフォーマンスには影響しないかもしれませんが、重度の場合や合併症がある場合は、人間工学に基づいた調整やフレキシブルなスケジュールなどの配慮が必要になるかもしれません。雇用主は、合理的な配慮を決定するために、従業員との双方向プロセスを行う必要があります。
脊柱側湾症の障害給付
脊柱側弯症の人は、社会保障障害保険(SSDI)や補足的保障所得(SSI)などの障害者給付を受ける資格があるかもしれません。脊柱側弯症の重症度とその機能的影響は、このプロセスで評価されます。

脊柱側湾症患者の法的保護
様々な法律が、脊柱側湾症患者を差別から保護し、機会均等を保障しています。ADAとリハビリテーション法は、雇用、公共サービス、公共宿泊施設において、平等なアクセスを確保するための合理的配慮を要求しています。
脊柱側弯症を障害と認識することへの挑戦
脊柱側弯症は人生に大きな影響を与える可能性がありますが、脊柱側弯症が単なる障害であるという考え方に挑戦することは重要です。脊柱側弯症患者の多くは、困難にもかかわらず充実した生活を送り、目標を達成しています。制限ではなく、能力に焦点を当てることで、脊柱側弯症患者への包括性とサポートを促進することができます。
結論
脊柱側湾症は、背骨の異常な湾曲を特徴とする。脊柱側弯症が障害とみなされるかどうかは、症状の重さや機能的能力への影響などの要因によって決まります。医学的な見地から脊柱側湾症は医学的な疾患として扱われ、一方、法的な枠組みは、影響を受けた人々に対する保護と便宜を提供します。日常生活や雇用への影響を認識し、必要なサポートを提供し、認識を改めることで、脊柱側弯症患者の包括性と機会均等を促進することができます。
参考文献
- 障害者給付金ヘルプ"脊柱側湾症で障害者給付金を申請する".障害者給付金ヘルプ.
- 側湾症研究会."側湾症の概要".側湾症研究会.
- 国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所。"脊柱側湾症".NIH.
- 米国雇用機会均等委員会。"1990年障害を持つアメリカ人法".EEOC。
- 社会保障庁."Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)".SSA.
- 国立衛生研究所。「1973年リハビリテーション法NIH.
- アメリカ整形外科学会。「脊柱側湾症を理解する.AAOS.
- メイヨークリニック「脊柱側湾症メイヨークリニック.
- WebMD."脊柱側湾症の症状と診断".WebMD.
- 脊椎健康財団「脊柱側湾症:原因と危険因子".脊椎健康財団.
- 障害者権利教育防衛基金。"障害を理解する".DREDF.
- 疾病予防管理センター。"関節炎の基礎知識".CDC.
- 米国国立生物工学情報センター。「脊柱管狭窄症とQOL(生活の質)。PubMed Central。
- 脊椎-健康「脊柱側弯症の日常生活への影響".Spine-Health.
- 全米側湾症財団."脊柱側湾症と雇用".全米側湾症財団.

