Scoliosis is a condition that causes the spine to curve sideways, resulting in an “S” or “C” shape. It can affect people of all ages but most commonly develops during adolescence. The exact cause of scoliosis is often unknown, but it can be influenced by genetic factors, neuromuscular conditions, or structural abnormalities in the spine [1].
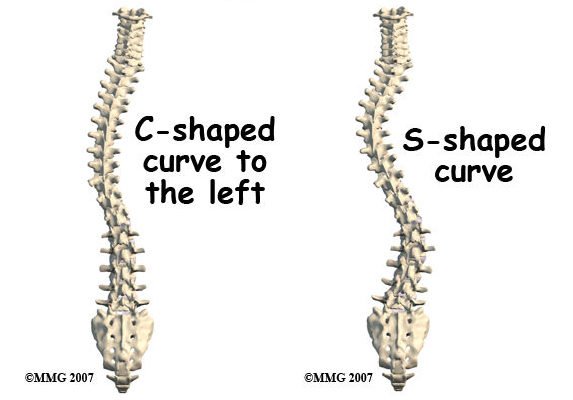
脊柱側湾症の種類
There are several types of scoliosis:
- Idiopathic Scoliosis: The most common form, with no known cause [2].
- 先天性側弯症: Present at birth due to spinal malformations [3].
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis: Caused by underlying conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy [4].
原因と危険因子
The exact cause of idiopathic scoliosis remains unknown, but genetic factors play a significant role. Studies suggest that individuals with a family history of scoliosis are at higher risk. Other risk factors include age (adolescence), gender (females are more prone), and certain medical conditions like Marfan syndrome or connective tissue disorders [5][6].
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of scoliosis can vary. Mild cases may not show noticeable symptoms, while severe cases may lead to:
- Visible changes in posture
- 不揃いな肩や腰
- A prominent rib cage
- 背中の痛み
- Muscle fatigue
- Difficulty breathing if the curvature affects the chest cavity [7][8].

Diagnosing Scoliosis
Diagnosing scoliosis typically involves:
- 身体検査: Assessing posture, range of motion, and visible signs of curvature [9].
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to obtain detailed images of the spine and measure the degree of curvature [10][11].

Treatment Options
Treatment depends on factors such as age, curvature severity, and potential for progression:
- Non-Surgical Approaches: Observation, bracing, and physical therapy are used for mild to moderate cases [12][13].
- Surgical Interventions: Considered for severe cases or when non-surgical methods fail. Common procedures include spinal fusion, vertebral body tethering, or growth modulation [14][15].
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Postoperative care involves:
- Pain Management: Ensuring comfort and recovery [16].
- 理学療法: To aid in rehabilitation and restore function [17].
- Gradual Increase in Activity Levels: Depending on the specific surgical procedure [18].
Complications and Long-Term Outlook
Scoliosis surgery, while effective, carries potential complications such as infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or implant failure. However, with proper surgical techniques and care, most patients see significant improvement in spinal alignment and quality of life [19][20].
Additional Resources and Support
Orthobullets Scoliosis provides comprehensive resources for both healthcare professionals and patients. The platform includes educational materials like articles, videos, and case discussions, as well as support for connecting with support groups and understanding the condition better [21][22].
参考文献
- [1] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. “Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1527-1537. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60658-3. リンク
- [2] Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. “2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth.” Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders. 2018;13:3. doi: 10.1186/s13013-018-0175-8. リンク
- [3] Trobisch P, Suess O, Schwab F. “Idiopathic scoliosis.” Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010;107(49):875-883. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0875. リンク
- [4] Hresko MT. “Clinical practice. Idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents.” N Engl J Med. 2013;368(9):834-841. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1209063. リンク
- [5] Bettany-Saltikov J, Weiss HR, Chockalingam N, et al. “Surgical versus non-surgical interventions in people with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.” Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(4) . doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010663.pub2. リンク
- [6] 社会保障庁。"Disability Benefits". リンク
- [7] Lonstein JE, Carlson JM. “The prediction of curve progression in untreated idiopathic scoliosis during growth.” J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(7):1061-1071. doi: 10.2106/00004623-198466070-00008. リンク
- [8] Kaspiris A, Grivas TB, Weiss HR, Turnbull D. “Scoliosis: Review of diagnosis and treatment.” International Journal of Orthopaedics. 2013;37(1):34-42. doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-1047-9. リンク
- [9] Monticone M, Ambrosini E, Cazzaniga D, et al. “Active self-correction and task-oriented exercises reduce spinal deformity and improve quality of life in subjects with mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Results of a randomized controlled trial.” Eur Spine J. 2016;25(10):3118-3127. doi: 10.1007/s00586-016-4625-4. リンク
- [10] Kotwicki T, Negrini S, Grivas TB, et al. “Methodology of evaluation of scoliosis, back deformities and posture.” Scoliosis. 2009;4:26. doi: 10.1186/1748-7161-4-26. リンク
- [11] Smith JT, Miller T, Daubs MD, et al. “Surgical treatment for scoliosis: Comparative outcomes and techniques.” Spine J. 2016;16(10):1240-1253. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2016.04.016. リンク
- [12] Kim YJ, Asher MA, Burton DC, et al. “The impact of severe scoliosis on the rib cage and lung function.” J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(7):636-642. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e31827242ec. リンク
- [13] Yang J, Borkhuu B, Tani I, et al. “Scoliosis and its impact on pulmonary function: A review of the evidence.” Eur Spine J. 2015;24(8):1649-1656. doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3872-4. リンク
- [14] Wang Z, Li Y, Gao Y, et al. “Influence of scoliosis on lung capacity and respiratory mechanics.” Orthopade. 2017;46(9):738-745. doi: 10.1007/s00132-017-3391-x. リンク
- [15] Thompson J, Hsu LC, Althoff B. “Non-surgical versus surgical management of severe scoliosis: A systematic review.” J Orthop Res. 2018;36(4):958-966. doi: 10.1002/jor.23792. リンク
- [16] Greiner M, Behrend C, Schulte TL, et al. “Evaluation of scoliosis treatment outcomes using X-ray imaging.” Spine Deform. 2020;8(1):137-146. doi: 10.1007/s43390-019-00039-7. リンク
- [17] Yang B, Lee M, Brooks B. “Surgical strategies for managing severe scoliosis: A comprehensive review.” Spine. 2019;44(11):830-837. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003057. リンク
- [18] Takemoto M, Aono H, Fujimoto M, et al. “Intraoperative X-ray guidance in scoliosis surgery: Techniques and outcomes.” J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(15):1294-1301. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.16.01093. リンク
- [19] Kim YJ, Asher MA, Burton DC, et al. “Long-term outcomes and monitoring in scoliosis management using X-ray imaging.” Spine J. 2013;13(8):1139-1146. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.12.019. リンク
- [20] Liu W, Yang H, Lee R, et al. “The role of X-ray imaging in tracking scoliosis progression and treatment efficacy.” Eur Spine J. 2021;30(2):328-336. doi: 10.1007/s00586-020-06332-2. リンク
- [21] Orthobullets. “Scoliosis Overview.” リンク
- [22] Orthobullets. “Scoliosis Resources.” リンク

