関節リウマチ(RA)は、主に関節を侵す自己免疫疾患である。免疫系が誤って体内の組織を攻撃し、関節に慢性的な炎症を引き起こすことで発症します。この炎症は痛み、こわばり、腫れを引き起こし、時間の経過とともに関節の変形や損傷をもたらすこともあります。約130万人のアメリカ人が関節リウマチを患っており、女性の有病率が高く、一般的に30~60歳の間に発症するといわれています。関節炎財団).

関節リウマチ側弯症とは?
脊柱側湾症は、背骨の異常な湾曲を特徴とする疾患で、多くの場合、直線ではなく「S」や「C」の形に似ています。この湾曲は、肩、腰、ウエストに目に見える凹凸を生じさせます。脊柱側湾症は人口のおよそ2~3%が罹患しており、ほとんどの症例は特発性、つまり原因が不明です。脊柱側湾症は思春期に診断されることがほとんどですが、どの年齢でも発症する可能性があります(側湾症研究会).
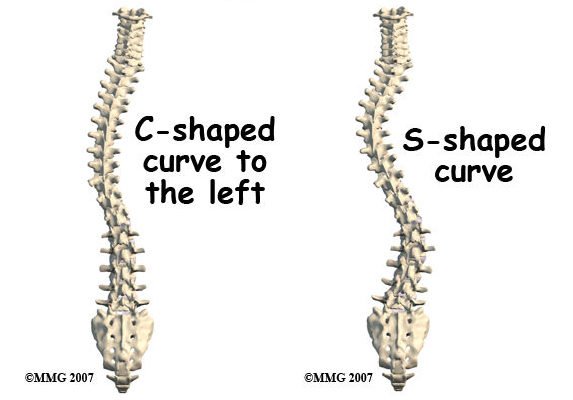
関節リウマチと脊柱側湾症の関連性
関節リウマチは、間接的に脊柱側弯症の発症や悪化につながる可能性があります。RAに伴う慢性炎症は、脊椎を支える靭帯や筋肉を弱め、脊椎の湾曲を引き起こす可能性がある。亜脱臼やびらんなど、RAに起因する関節の変形もまた、脊柱のアライメントを変化させ、脊柱側弯症の一因となる可能性がある(臨床リウマチ学雑誌).
関節リウマチと脊柱側湾症の共通症状
関節リウマチの症状には、関節の痛み、こわばり、腫れ、疲労などがあります。これらの症状は一般的に左右対称であり、重症例では関節の変形や機能喪失につながることもあります(国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所).脊柱側湾症では、特に湾曲がひどい場合、腰や肩の凹凸、肩甲骨の突出、背中の痛みなどの症状が現れます(脊椎の健康).
関節リウマチと脊柱側湾症の診断
関節リウマチの診断には、病歴聴取、身体診察、特異的抗体の血液検査や関節損傷の画像検査などの診断検査が含まれる(米国リウマチ学会).脊柱側湾症では、身体検査とX線検査で脊椎の湾曲を評価し、診断を確定する(側湾症研究会).

関節リウマチ側弯症の治療法
関節リウマチの治療は、炎症を抑え、痛みを和らげ、関節の損傷を遅らせることに重点を置いています。一般的な治療法としては、NSAIDs、DMARDs、生物学的製剤(関節炎財団).脊柱側湾症の治療には、湾曲の程度に応じて、理学療法、装具、手術が行われます(全米側湾症財団).
関節リウマチの治療薬 脊柱側湾症
RA治療薬には、炎症を抑え、痛みを抑えるNSAIDsやDMARDsがある。重症例では生物学的製剤が使用されることもある(米国リウマチ学会).脊柱側弯症の場合、通常、薬は主な治療法として使用されることはないが、それに伴う不快感に対して鎮痛剤が処方されることがある(脊椎の健康).
関節リウマチの理学療法と運動 脊柱側湾症
理学療法は、RAと脊柱管狭窄症を管理するために非常に重要である。RAでは、運動や手技を通して関節の可動性を改善し、痛みを軽減します。国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所).脊柱側湾症に対しては、姿勢を改善し、脊柱を支える筋肉を強化し、柔軟性を高めることを目的とした治療を行う(側湾症研究会).
関節リウマチ側弯症に対する外科的介入
重度のRAでは、痛みを和らげ機能を回復させるために人工関節置換術が必要になることもある(関節炎財団).脊柱側湾症の場合、重度の湾曲を矯正し脊椎を安定させるために脊椎固定術が一般的に行われる(全米側湾症財団).
関節リウマチ側弯症に対する生活習慣の改善
両疾患の管理には、生活習慣の改善が重要な役割を果たす。RAでは、健康的な体重を維持し、バランスのとれた食事をとり、喫煙を避けることが有効である(関節炎財団).脊柱側湾症には、良い姿勢を保つこと、定期的な運動、重いものを持たないことが重要である(脊椎の健康).
結論関節リウマチと脊柱側弯症の管理
関節リウマチと脊柱管狭窄症の関係を理解することは、効果的な管理のために不可欠です。どちらの症状も治療法はありませんが、様々な治療法や生活習慣の改善によって症状を緩和し、生活の質を向上させることができます。医療従事者と密接に協力することで、個人に合った治療計画を立て、これらの症状を効果的に管理することができます(米国リウマチ学会).
参考文献
- 関節炎財団"関節リウマチとは何ですか?"関節炎財団。2024年8月にアクセス。
- 側湾症研究会「側湾症とは?側湾症研究会.2024年8月アクセス。
- 臨床リウマチ学会誌。「関節リウマチと脊柱側弯症:総説".2024年8月アクセス。
- 国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所。"関節リウマチ".国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所.2024年8月アクセス。
- 脊椎の健康「脊柱側湾症の概要スパインヘルス.2024年8月アクセス。
- 米国リウマチ学会。"RAの診断と治療".米国リウマチ学会。2024年8月アクセス。
- 全米側湾症財団."側湾症治療".全米側湾症財団.2024年8月アクセス。
- 国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所。"RAの理学療法".国立関節炎・筋骨格系・皮膚疾患研究所。2024年8月アクセス。
- 脊柱側湾症研究会。「脊柱側湾症の理学療法".側湾症研究会.2024年8月アクセス。
- 関節炎財団。"RA治療の選択肢"関節炎財団。2024年8月アクセス。
- 脊椎の健康「脊柱側湾症の治療.スパインヘルス.2024年8月アクセス。
- 全米側湾症財団.「側湾症手術.全米側湾症財団.2024年8月アクセス。
- 関節炎財団。"RAのためのライフスタイルの修正"。関節炎財団。2024年8月アクセス。
- 脊椎の健康「脊柱側湾症と共に生きる.Spine Health.2024年8月アクセス。
- 米国リウマチ学会。"RA患者リソース".米国リウマチ学会。2024年8月アクセス。

